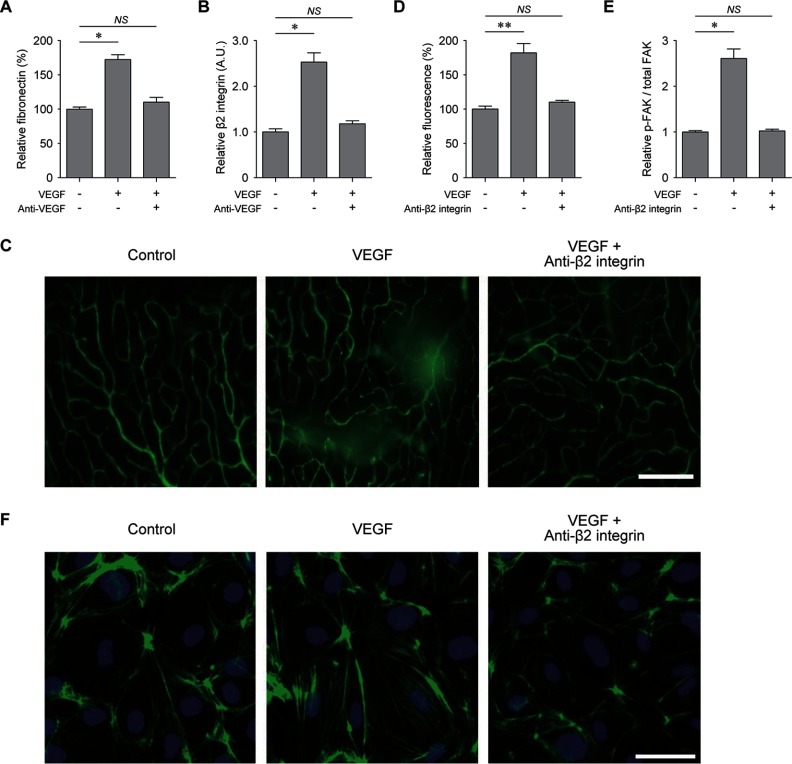
Fig. 3.
Inhibition of VEGF-induced vascular leakage by anti-β2 integrin antibody. A, levels of fibronectin in the retina measured by ELISA. Anti-VEGF, VEGF plus anti-VEGF antibody (n = 4). B, levels of β2 integrin in the retina measured by Western blotting analysis (n = 3). C, qualitative assessment of retinal vascular integrity demonstrated by the leakage of FITC-dextran after treatments of PBS (control), VEGF (VEGF), and VEGF plus anti-β2 integrin antibody (anti-β2 integrin). D, quantitative analysis of relative fluorescence intensity after treatments of VEGF (VEGF) and VEGF plus anti-β2 integrin antibody (anti-β2 integrin) (n = 4). E, levels of phosphorylated FAK normalized by the total amount of FAK (p-FAK/total FAK) in confluent HRMECs on FN1-coated dish at 5 min after treatments of VEGF (VEGF) and VEGF plus anti-β2 integrin antibody (Anti-β2 integrin) (n = 4). F, actin cytoskeleton arrangement after treatments of PBS (Control), VEGF (VEGF), and VEGF plus anti-β2 integrin antibody (Anti-β2 integrin) demonstrated by immunofluorescence staining of F-actin (green). Nucleus was identified with DAPI staining. NS, p > 0.05; *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01 using Kruskal-Wallis test with post hoc Dunn's multiple comparison test.