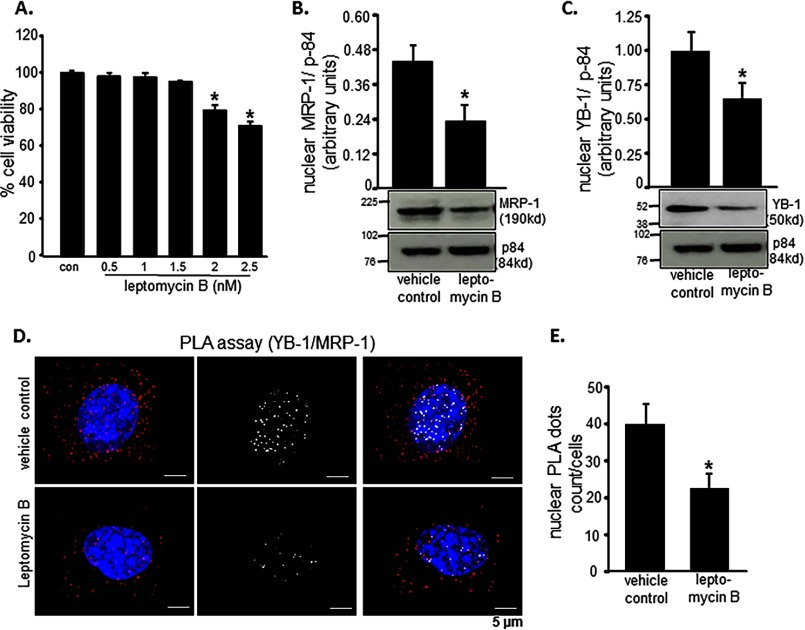
FIGURE 7.
MRP-1 nuclear translocation is YB-1-dependent. Leptomycin B was used to inhibit nuclear translocation. A, toxicity was evaluated by LDH assay, and 4-h treatment with 2 nm leptomycin B resulted in loss of cell survival. B and C, Western blotting images show that 4-h treatment with leptomycin B (2 nm) causes a significant reduction in MRP-1 (B) and YB-1 (C) protein expression. Protein-protein interaction between MRP-1 and YB-1 inside the EOMA cell nucleus was demonstrated using an in situ PLA. D, treatment with leptomycin B (2 nm, 4 h) resulted in a significant reduction of PLA-positive signals (red dots) with those interactions specifically occurring in the nucleus by co-localization of red dots and blue DAPI staining and represented by white dots. E, quantification of nuclear PLA events reveals that roughly 50% of the interaction between MRP-1 and YB-1 was inhibited by 2 nm leptomycin B treatment for 4 h. Results are expressed as mean ± S.D. (error bars); *, p < 0.05.