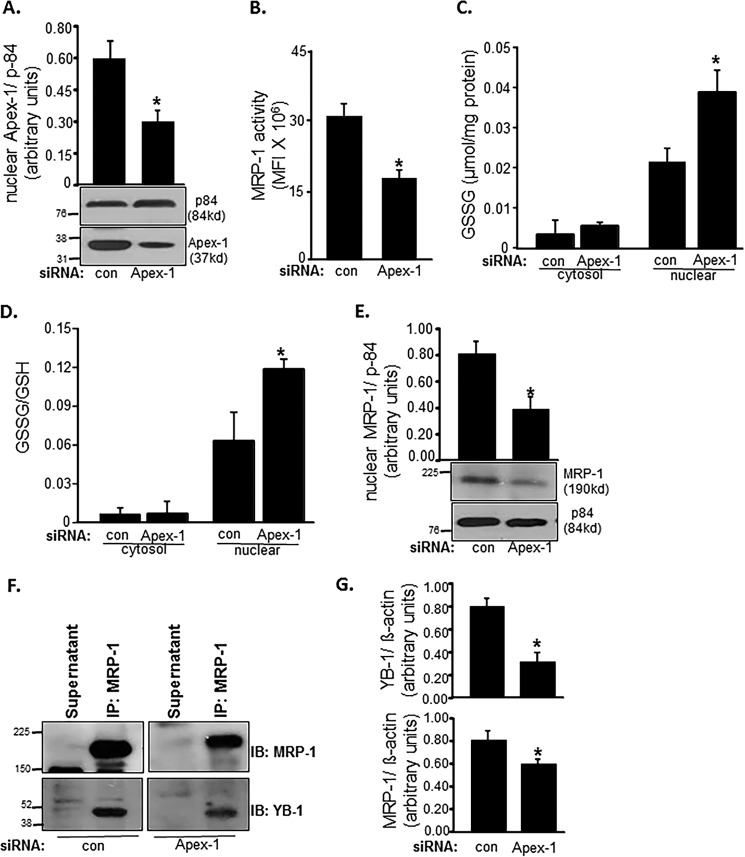
FIGURE 8.
MRP-1 function is Apex-1-dependent. apex-1 knockdown in EOMA cells resulted in a significant decrease of nuclear Apex-1 protein expression (A). MRP-1 activity as measured by calcein exclusion is also decreased in apex-1 knockdown cells (B). apex-1 knockdown resulted in a significantly elevated nuclear GSSG level (C) as well as ratio of oxidized to reduced glutathione (D) in the nucleus of EOMA cells compared with transfection controls. Western blotting demonstrates significantly decreased nuclear MRP-1 protein expression in apex-1 knockdown cells (E). F, association of MRP-1 with YB-1 was identified in apex-1 knockdown EOMA cells by the immunoprecipitation (IP) technique described previously. The cell lysates of control and apex-1 siRNA-treated EOMA cells were subjected to immunoprecipitation with MRP-1 antibody. The immunoprecipitates were separated by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted (IB) for MRP-1 and YB-1 with densitometry analysis of both proteins showing an apex-1-dependent decrease in protein expression (G). Results are expressed as mean ± S.D. (error bars); *, p < 0.05.