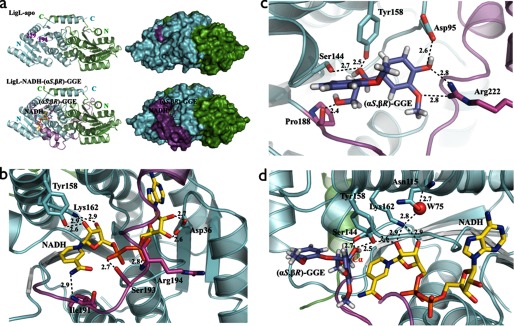
FIGURE 3.
a, schematic and molecular surface representations of apo-LigL and the LigL·NADH·(αS,βR)-GGE complex. The substrate binding loop (residues 191–229) is completely disordered in the apo-LigL structure. In the LigL·NADH·(αS,βR)-GGE complex structure the substrate binding loop region (magenta) acts as a lid above the NADH and GGE binding sites. b, the active site of LigL in complex with NADH showing the interactions involving the co-substrate NADH. Residue Asp36 contacts the 2′- and 3′-hydroxyl groups of the adenosine ribose sugar, the catalytic residues Tyr158 and Lys162 contact the nicotinamide ribose sugar, the nicotinamide moiety interacts with the main chain nitrogen atom from Ile191, and the phosphate groups interact with side chain atoms from Ser193 and the main chain nitrogen atom from Arg194. c, the substrate binding site for LigL·NADH·(αS,βR)-GGE showing residues Asp95, Ser144, Tyr158, Pro188, and Arg222 that interact directly with the GGE substrate. d, active site of LigL·NADH·(αS,βR)-GGE showing the catalytic tetrad N115-S144-Y158-K162 and a water molecule (W75) involved in the extended proton relay system described for the SDR family (24). Broken lines represent hydrogen bonds, and distances are shown in Å.