FIGURE 1.
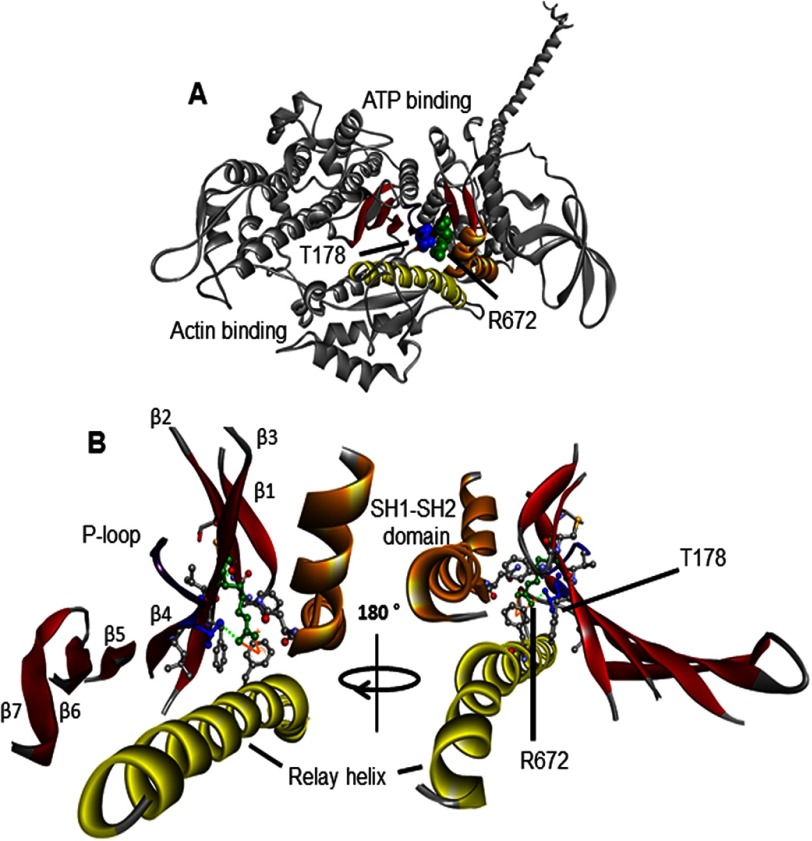
Homology model of embryonic myosin S1. This ribbon structure is based on the scallop structure in the pre-power stroke conformation (PDB code 1QVI). A, the myosin heavy chain is shown in gray, the SH1-SH2 helices in orange, the relay helix in yellow, the P-loop in purple, and the seven-stranded β-sheet in red. The arginine 672 (R672) and threonine 178 (T178) residues are shown in green and blue space filling mode, respectively. Both of these residues are highly conserved across species and myosin isoforms, including the scallop myosin and human MyHC-emb. Both residues are in the center of the S1 domain located in the upper 50-kDa domain near the ATP binding cleft. B, enlargement of the region around Arg672 (located on the third β-strand) and Thr178 on the fourth β-strand of the seven-stranded β-sheet that runs through the S1 domain. Thr178 is also at the base of the P-loop (GESGAG, residues 179–184), which is involved in ATP binding. The green dotted line represents hydrogen bonds that can be seen between Thr178 and Arg672, whereas the solid orange line indicates a π-cation bond that can be seen between Arg672 and Phe490. The interactions of Arg672 and Thr178 are summarized in Tables 2 and 3. Residues not labeled are those found to interact with either Arg672, Thr178, or both and are summarized in Tables 2 and 3.