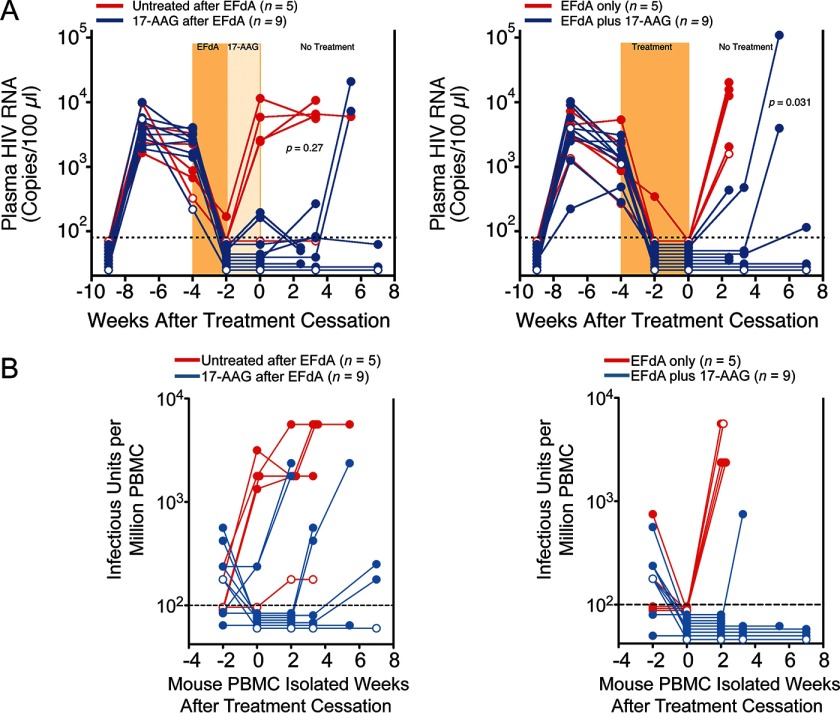
FIGURE 2.
Hsp90 inhibition prevents virus rebound for several weeks after treatment cessation. A, groups of viremic HIVJR-CSF-infected NSG-BLT mice were treated orally once a day with 10 mg/kg/day EFdA for 2 weeks (left) or 4 weeks (right). Separate groups were treated by twice-daily subcutaneous injection of 17-AAG (10 mg/kg/day) for 2 weeks either after EFdA (left) or concurrent with EFdA for the last 2 weeks (right). The treatment period is indicated by shading, and mice in both comparisons were from the same NSG-BLT mouse cohort. Mouse peripheral blood human CD4+ T cell counts at the time of treatment cessation were highly similar between groups with means of 100 CD4+ T cells/μl (untreated after EFdA), 210 CD4+ T cells/μl (17-AAG after EFdA), 130 CD4+ T cells/μl (EFdA only), and 130 CD4+ T cells/μl (EFdA plus 17-AAG). p values for Fisher's exact test for rebounders versus nonrebounders were determined at the last blood collection. B, IUPM assay on mouse PBMC samples from mice treated with EFdA followed by 17-AAG (left) and mice treated simultaneously with EFdA and 17-AAG for the experiment shown in Fig. 6A. Sample testing began 2 weeks before treatment cessation and continued until mouse termination. Open circles, mice that were not injected with CD34+ hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells. Data for EFdA-only control mice in A were published previously (46).