FIGURE 9.
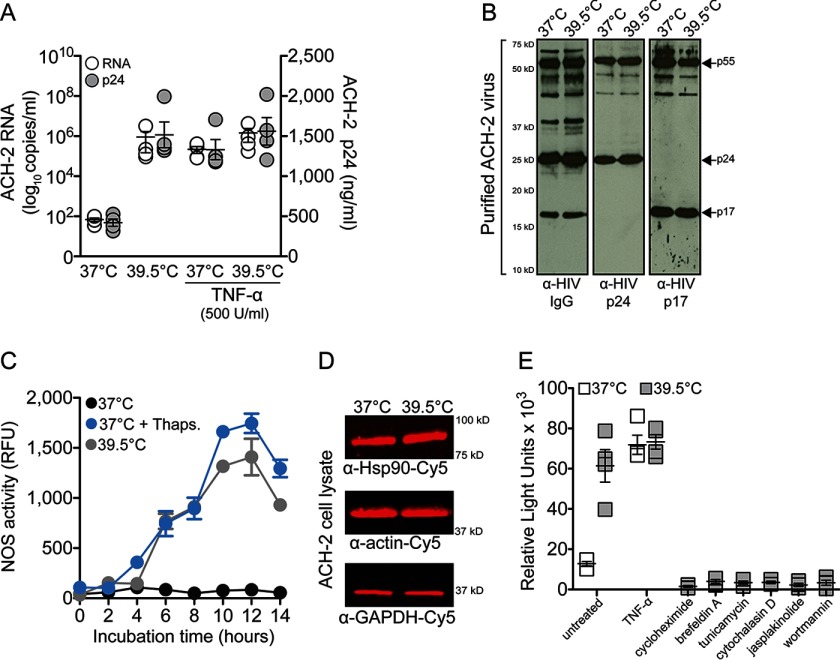
Heat shock (39.5 °C) accelerates HIV transcription in persistently infected ACH-2 cells. A, HIV RNA and p24 levels in culture supernatants from ACH-2 cells incubated at 37 and 39.5 °C. TNF-α was used to activate HIV transcription at 37 °C. p < 0.001 comparing ACH-2 p24 at 37 °C with ACH-2 p24 at 39.5 °C, 37 °C + TNF-α, and 39.5 °C + TNF-α by Student's t test. Data represent mean ± S.E. (n = 4). B, Western blotting analysis of the purified ACH-2 virions. C, nitric-oxide synthase activity in ACH-2 cells at 37 and 39.5 °C; thapsigargin was used as a positive control at 37 °C. Results represent mean ± S.E. (error bars) (n = 3). D, quantitative fluorescence Western blotting analysis of ACH-2 cell lysates. Results are representative of four independent experiments. E, TZM-bl luciferase assay of TZM-bl cells inoculated with an equal volume of culture supernatants from ACH-2 cells treated with the indicated agents. p = 0.001 comparing ACH-2 infectivity at 37 °C with ACH-2 infectivity at 39.5 °C by Student's t test. Data represent mean ± S.E. (n = 3).