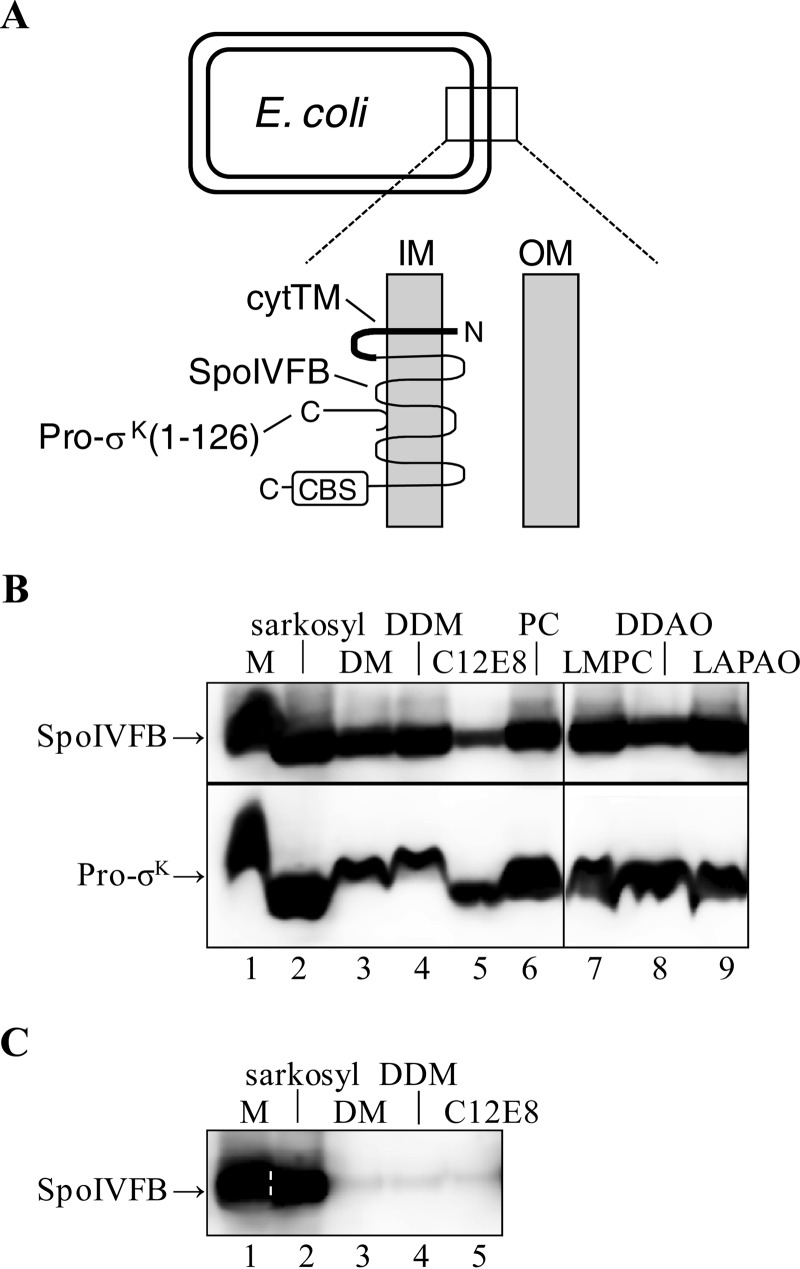
FIGURE 2.
Coexpression of Pro-σK(1–126)-His6 and SpoIVFB in E. coli and effect on solubilization of SpoIVFB from membranes. A, E. coli cell and an expanded view of the inner (IM) and outer membrane (OM). Pro-σK(1–126)-His6 associates peripherally with the inner membrane (45). The topology of SpoIVFB was determined previously (77). SpoIVFB has a C-terminal CBS domain, and in some experiments an extra TMS (cytTM) was added to its N-terminal end. B, solubilization of coexpressed proteins. E. coli bearing pYZ42 was grown in a fermentor and induced with IPTG to coexpress Pro-σK(1–126)-His6 and SpoIVFB-TEV-FLAG2 E44Q. The membrane (M) fraction from 5 g of cells was untreated or treated with the indicated detergent to solubilize proteins. After high-speed centrifugation, the supernatant was subjected to immunoblot analysis with anti-FLAG (top) or anti-His (bottom) antibodies. PC, n-dodecylphosphocholine; LMPC, 1-myristoyl-2-hydroxy-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine; DDAO, n-dodecyl-N,N-dimethylamine-N-oxide; LAPAO, 3-dodecylamido-N,N′-dimethylpropyl amine oxide. C, solubilization of enzyme alone. This is the same as in A, except pYZ50 was used to express cytTM-SpoIVFB-TEV-FLAG2-His6 alone, and immunoblot analysis was done with only anti-FLAG antibodies. A dashed white line was added to help visualize the demarcation between lanes 1 and 2. In both panels, representative results from at least two biological replicates are shown.