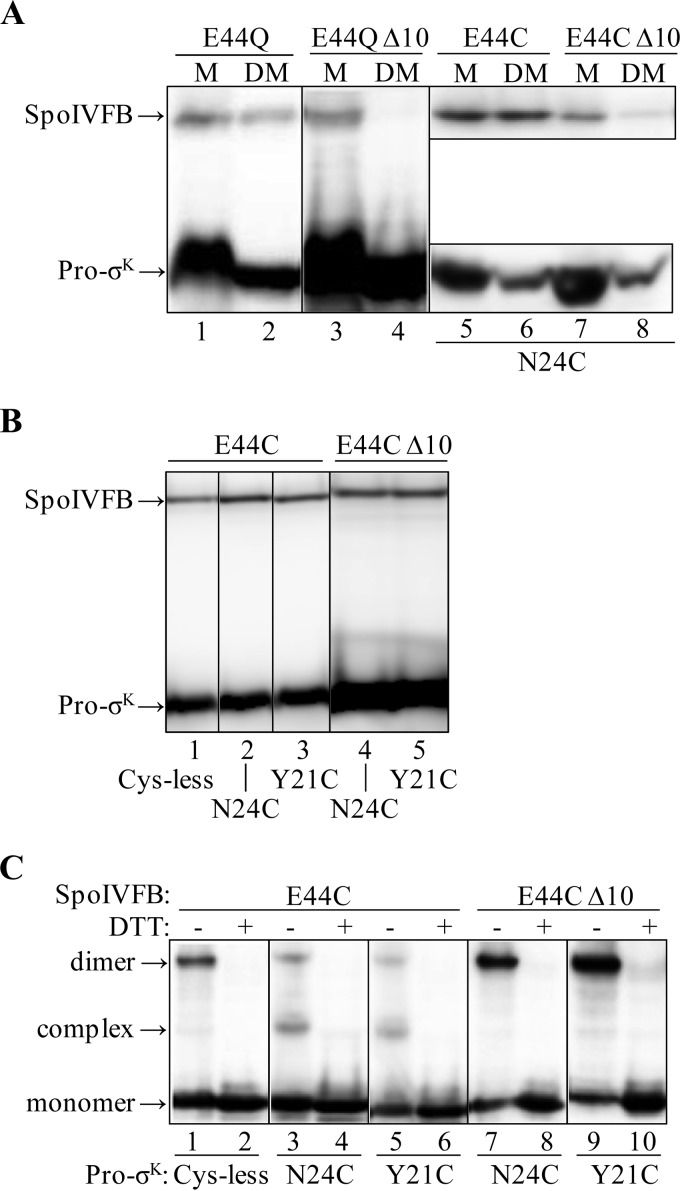
FIGURE 4.
Effects of deleting the last 10 residues of SpoIVFB. A, effects of Pro-σK(1–126) coexpression on the solubilization of TM-SpoIVFB from membranes. E. coli bearing pBS236 and pZR262 (lanes 1 and 2), pJZ7 and pZR262 (lanes 3 and 4), pYZ40 and pZR241 (lanes 5 and 6), or pYZ49 and pZR241 (lanes 7 and 8) were cultured (1 liter) and induced with IPTG to coexpress versions of TM-SpoIVFB, indicated at the top, and Pro-σK(1–126)-FLAG2 (lanes 1–4) or single-Cys Pro-σK(1–126)-His6 N24C (lanes 5–8). The membrane (M) fraction was treated with DM to solubilize the proteins followed by high-speed centrifugation and collection of a sample of the supernatant (DM). Samples were subjected to immunoblot analysis with anti-FLAG (lanes 1–4 and 5–8, top) or anti-His (lanes 5–8, bottom) antibodies. B, expression of proteins. E. coli bearing pYZ40 and pZR99 (lane 1), pYZ40 and pZR241 (lane 2), pYZ40 and pPL12 (lane 3), pYZ49 and pZR241 (lane 4), or pYZ49 and pPL12 (lane 5) were cultured (10 ml) and induced with IPTG to coexpress single-Cys versions of TM-SpoIVFB, indicated at the top, and Cys-less or single-Cys versions of Pro-σK(1–126)-His6, indicated at the bottom. Cell extracts were subjected to immunoblot analysis. Both proteins were detected with anti-His antibodies. C, disulfide cross-linking in vivo. E. coli bearing the same plasmid combinations and induced as in B were treated with 1 mm Cu2+(phenanthroline)3 for 10 min. Proteins were precipitated with TCA and resuspended in sample buffer with or without DTT as indicated. Antibodies against the FLAG tag on TM-SpoIVFB were used to detect monomer, complex with Pro-σK(1–126)-His6, and dimer. The results are presented in the same order as in B (two lanes for each plasmid combination). In A–C, representative results from at least two biological replicates are shown.