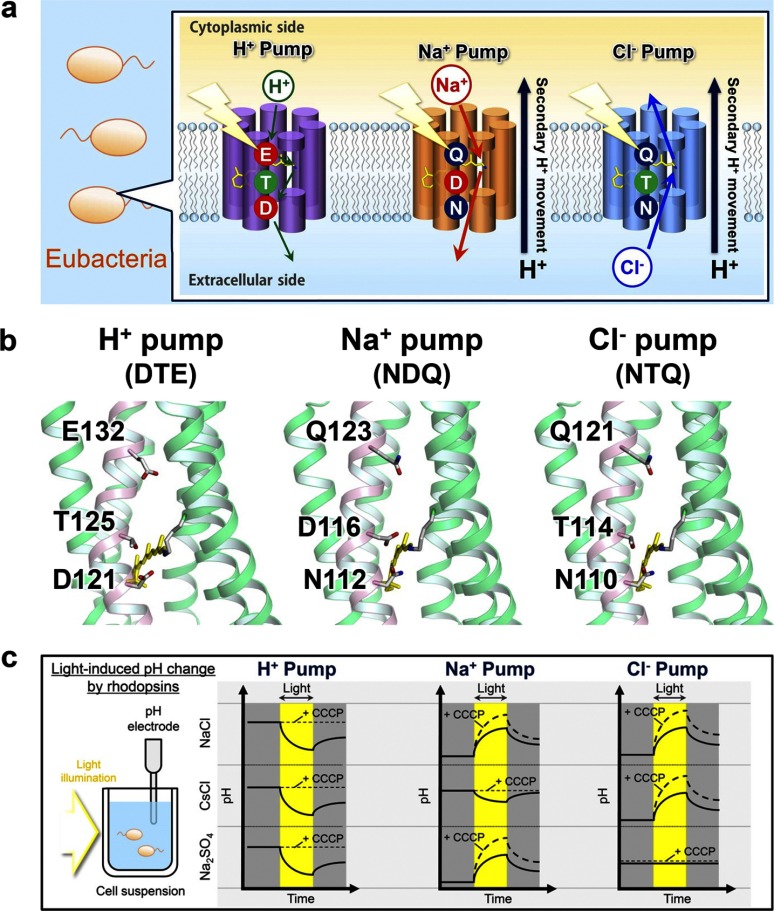
FIGURE 1.
Light-driven ion-pumps in eubacteria and their transport activity. a, eubacterial rhodopsins contain DTE, NDQ, and NTQ motifs for H+, Na+, and Cl− pumps, respectively. b, motifs in GR, KR2, and FR based on the structure of XR (left, PDB ID: 3DDL) and KR2 (middle, right, PDB ID:3X3C). c, ion pumping activity assayed by pH changes. Light-driven H+ pump shows pH decrease in the presence of any ions, which is diminished by a protonophore CCCP. In contrast, Na+ and Cl− pumps cause pH increase, which is enhanced by CCCP. Light-driven Na+ and Cl− pumps are distinguished by their cation- and anion-dependent transport, respectively.