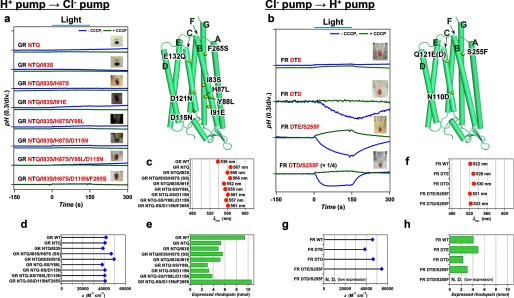
FIGURE 5.
Optimization of functional conversions between light-driven H+ and Cl− pumps by additional mutations outside of the conserved helix C motifs. Unsuccessful functional conversion of H+ → Cl− pump in GR (a) and successful functional conversion of Cl− → H+ pump in FR (b) in the presence of 100 mm NaCl (pH ∼7.0) in the absence (blue) and presence (green) of CCCP, respectively. The positions of mutations are indicated by yellow spheres in the modeled structure (right), and the names of helices are shown with green characters. The λmax (c, f), ϵ (d, g) and the amount of expressed rhodopsin in the E. coli cell used for the pump activity assay (e, h) of wild type and mutant proteins.