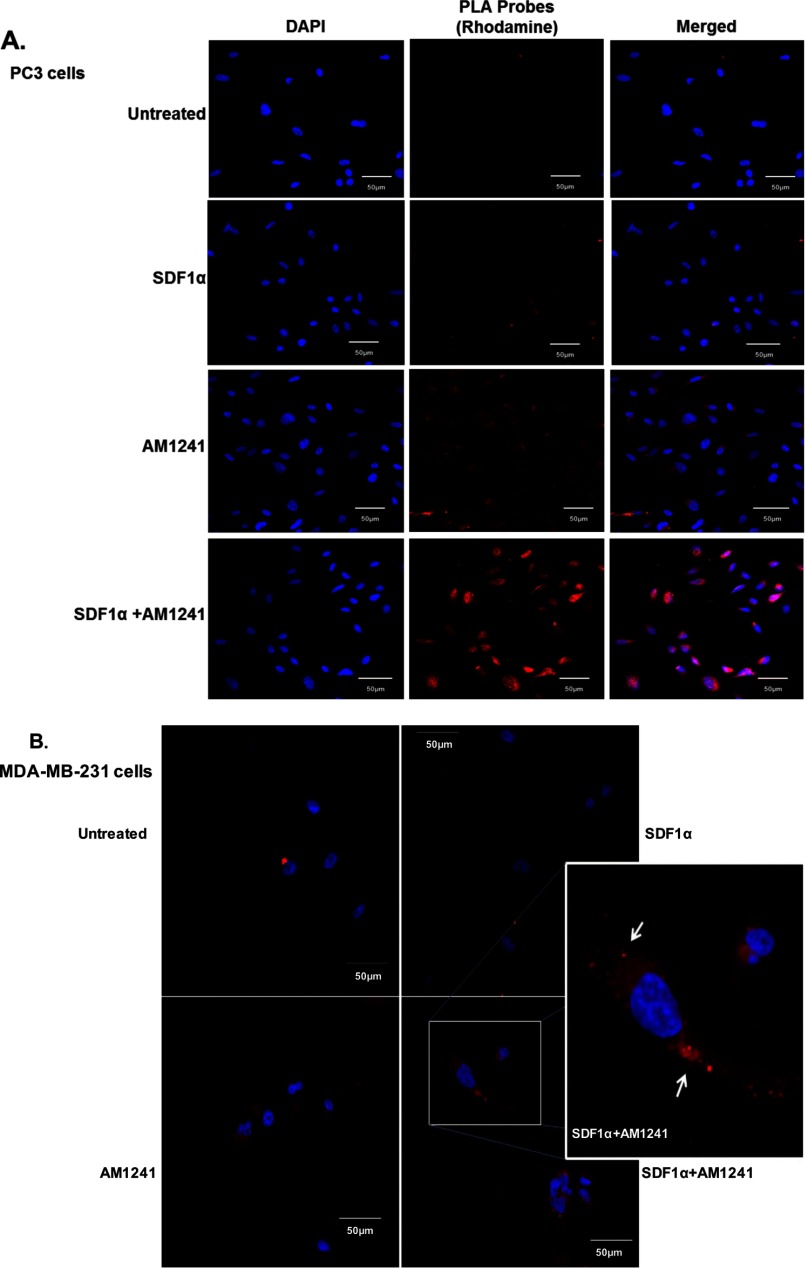
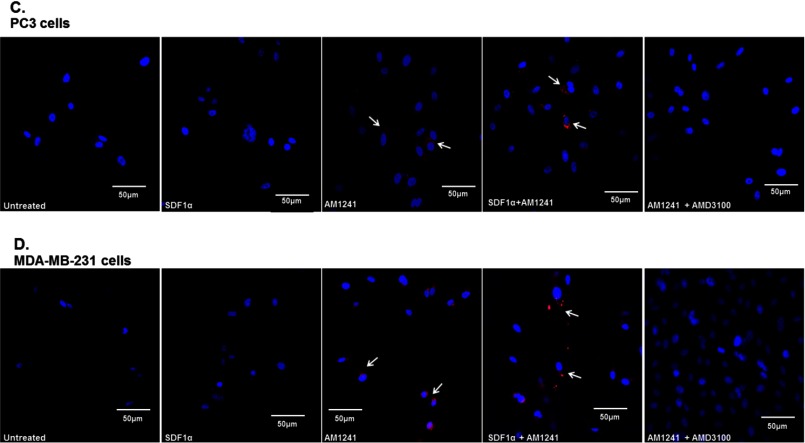
FIGURE 4.
Endogenous CXCR4 and CB2 formed heterodimers in cancer cells. Heterodimerization of CXCR4 and CB2 was recognized by incubating cells with primary antibodies raised in two different species and secondary antibodies linked to different DNA oligomers, one designated PLUS and one designated MINUS. If the two receptors were close enough, the two different antibody-DNA probes were able to ligate and hybridize. Following an amplification process, the presence of fluorescently tagged nucleotides allowed detection of a punctate fluorescence signal by confocal microscopy. PC3 (A) and MDA-MB-231 (B) cells were each plated on coverslips; serum-starved for 24 h; and then treated with SDF1α, AM1241, or SDF1α/AM1241 simultaneously for 1 min prior to fixing with methanol (PC3) or 2% paraformaldehyde (MDA-MB-231). Cells were prepared as described above (Duolink). A CXCR4/CB2 heterodimer was detected via positive ligation of PLA probes on a rhodamine filter (excitation, 571 nm; emission, 590 nm), and nuclei were stained with DAPI. Images were reviewed and captured using a Zeiss LSM 700 confocal microscope. Scale bars, 50 μm. B, merged images of MDA-MD-231 cells only; colocalization and heterodimerization in merged images are indicated by punctate foci and white arrows. Designated PC3 (C) or MDA-MBA-231 (D) cells were pretreated with AMD3100 (1 μg/ml) prior to treatment with SDF1α and/or AM1241. Cells were later harvested for Duolink as described above. Magnification, 20×; scale bars, 50 μm. Each experiment was performed at least twice.