FIGURE 3.
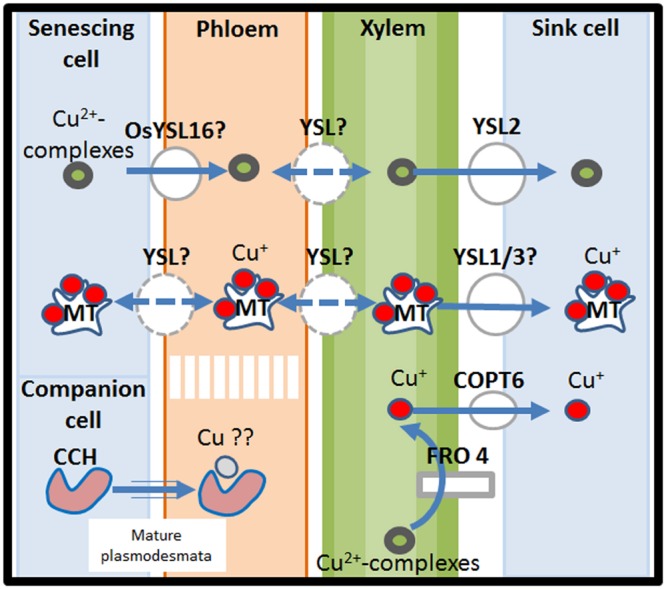
A model of the long-distance system for Cu-transport. Copper ions are transported in the vasculature in the form of Cu(I)-MT or Cu(II)-complexes. Prior to leaf cellular uptake, Cu2+ is reduced to Cu+ by FRO4 and enters the leaf cell by COPT6 proteins. Cu remobilization from senescing tissues is performed via YSL proteins. In particular YSL proteins similar to YSL16 in O. sativa are involved in the transport of Cu from Cu(II)-complexes from senescing organs to the phloem. A possible involvement of CCH in Cu remobilization from old to young tissues has also been envisaged. Remobilized-Cu is transferred to sink organs via YSL-proteins such as YSL2 for the transport of Cu(II)-complexes and probably YSL1/3 for Cu(I)-MT transport. CCH, Cu chaperone; COPT6, Cu transporter 6; FRO4, ferric reductase oxidase 4; MT, metallothioneins; YSL, Yellow Stripe Like.
