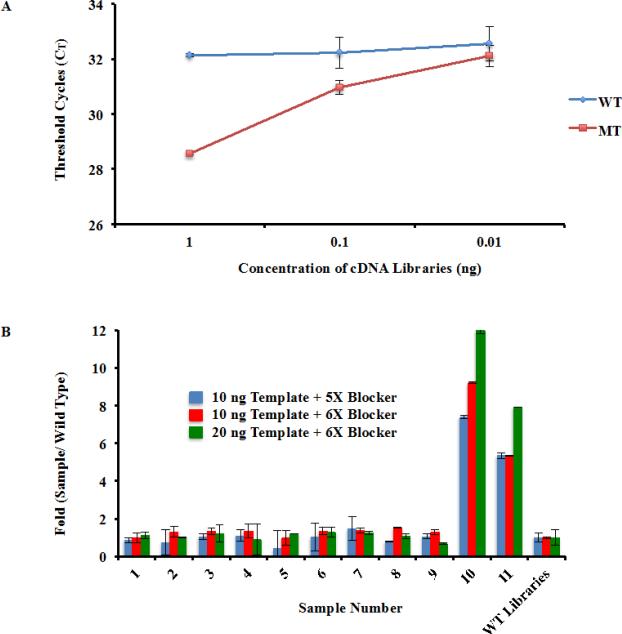
Fig. 4.
Identify the H3.3K27M mutation within cDNA libraries. (a) Amplification selectivity using cDNA libraries prepared from samples containing wild type and mutant H3F3A allele. The PCR conditions established in Fig. 3 was used to amplify three different amounts of cDNA libraries (1 ng, 0.1 ng, and 0.01 ng). (b) Identify samples containing H3F3A K27M mutation using the optimized procedure. To simulate actual medical situations, cDNA libraries from eleven different patient samples were gathered, two of which contained the H3F3A K27M mutation. This information was kept unknown from RZ during testing. The optimal qPCR conditions were used to blindly analyze all eleven samples using two different template and blocker oligo concentrations. The differences in amplification (fold changes) between a sample containing wild type H3F3A and each of the 11 patient samples were calculated.