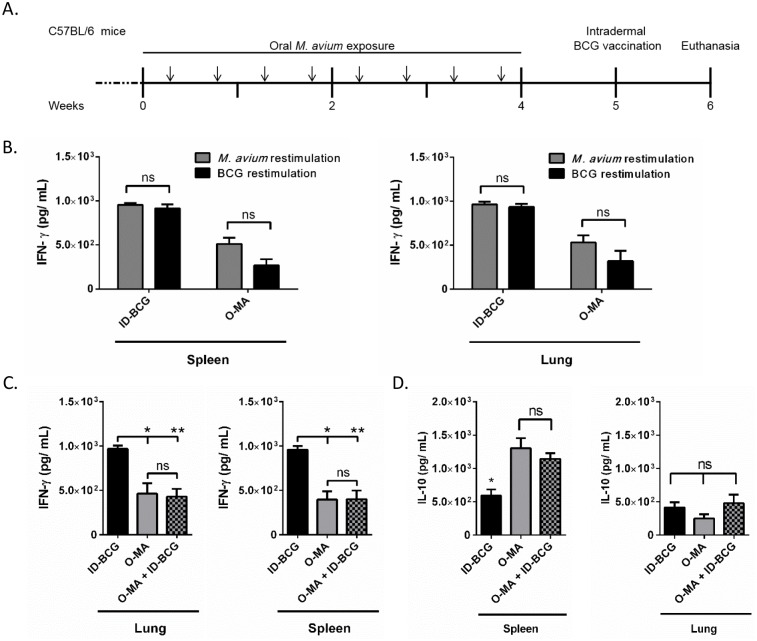
Fig 1. Differences in cytokine response to BCG immunization were observed between mice that were or were not presensitized to oral M. avium prior to intradermal BCG vaccination.
(A) Experimental design. Arrows indicate M. avium exposure. (B) Interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) secretion in response to restimulation of splenic and lung T cells from mice exposed to either intradermal BCG or oral M. avium with either heat-killed whole BCG or M. avium, n = 6. (C) IFN-γ secretion in response to heat-killed whole BCG antigen restimulation of splenic and lung T cells from different treatment groups, n = 6. (D) Interleukin-10 (IL-10) secretion in response to BCG restimulation of splenic and lung T cells from groups intradermally immunized with BCG with and without oral M. avium presensitization, n = 3. A Mann-Whitney U test or multiple t-tests (Holm-Sidak) were used for comparison of two data sets, and a one-way ANOVA Kruskal-Wallis with Dunn’s multiple comparison post-test for multiple data sets. *p < .05; **p < .01; data shown with standard error of the mean (SEM). Abbreviations: Intradermal BCG only (ID-BCG), oral M. avium only (O-MA), oral M. avium presensitization with intradermal BCG vaccination (O-MA + ID-BCG).