Fig 1. Three maternal factors regulate initial zygotic gene expression.
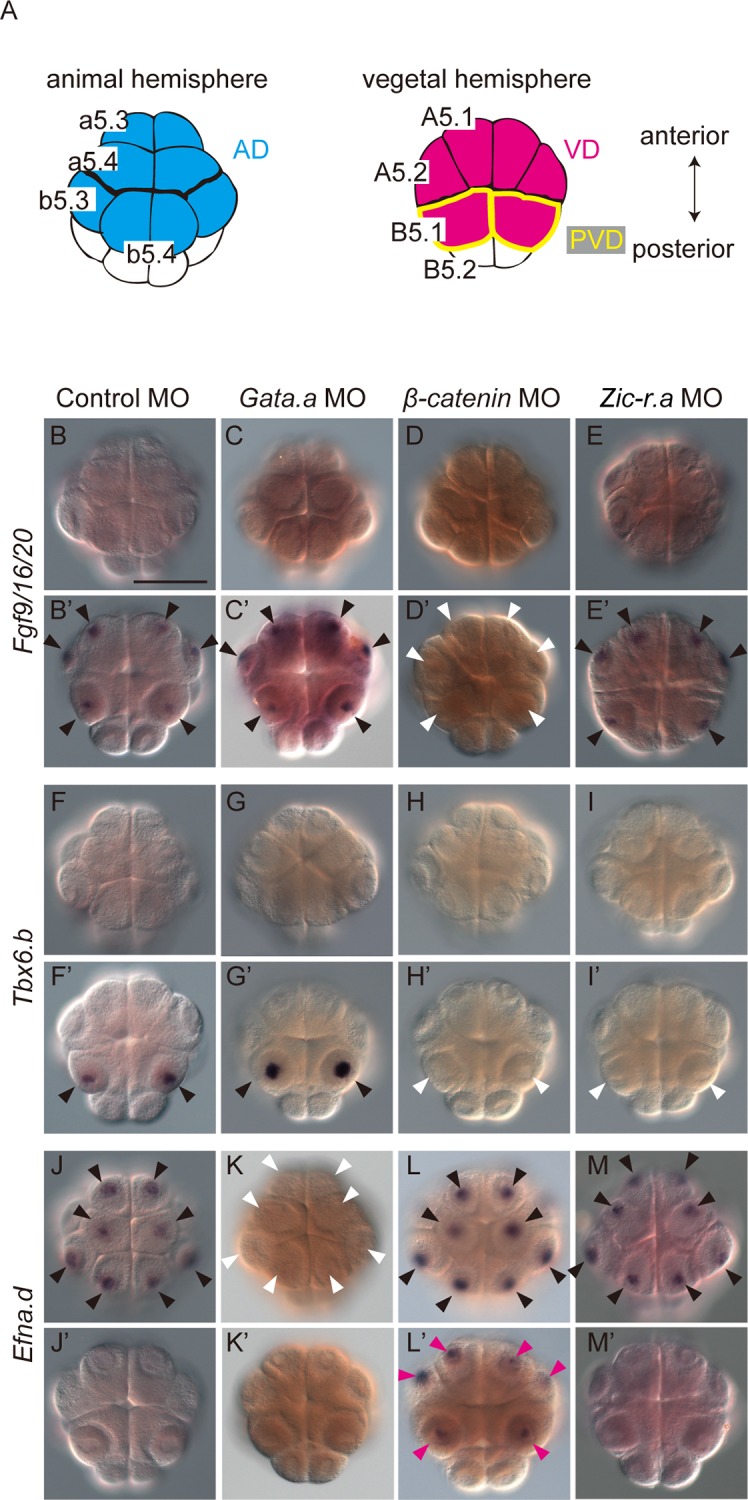
(A) Schematics of the animal and vegetal hemispheres of the bilaterally symmetrical 16-cell embryo. Blastomere names are indicated in the left half of the bilaterally symmetrical embryo. Cell names in the animal hemisphere domain (AD; light blue) begin with a small letter. Cell names in the vegetal hemisphere domain (VD; magenta) begin with a capital letter. The posterior vegetal domain (PVD) consists of a pair of cells named B5.1, which are enclosed by yellow lines. (B–M) Expression of (B-E, B’-E’) Fgf9/16/20, (F–I, F’–I’) Tbx6.b, and (J–M, J’–M’) Efna.d in 16-cell embryos injected with (B, B’, F, F’, J, J’) a control MO, (C, C’, G, G’, K, K’) Gata.a MO, (D, D’, H, H’, L, L’) β-catenin MO, or (E, E’, I, I’, M, M’) Zic-r.a MO. White arrowheads indicate loss of expression. Magenta arrowheads indicate ectopic expression. (B–M) Animal views and (B’–M’) vegetal views are shown. Scale bar, 100 μm.
