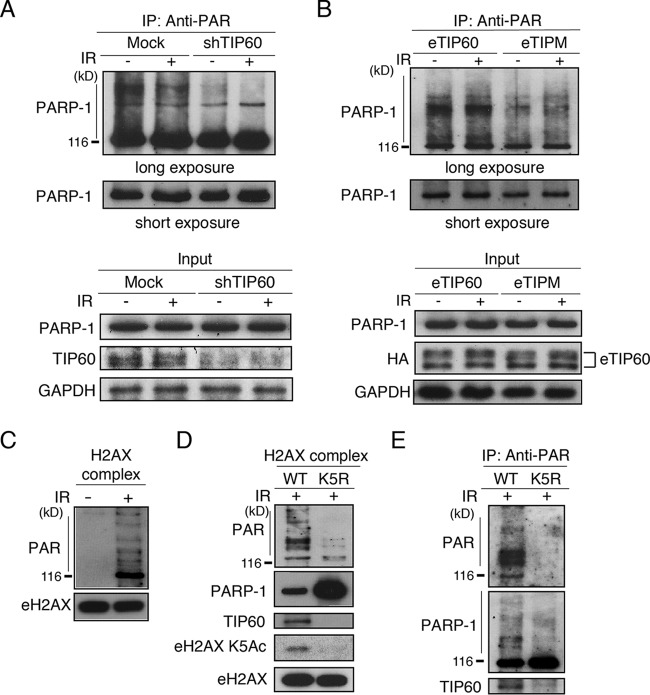
FIG 3.
K5 acetylation of H2AX is required for efficient auto-poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation of PARP-1 upon DNA damage response. (A) Anti-PAR antibody immunoprecipitates were subjected to an immunoblot analysis using an anti-PARP-1 antibody. Unirradiated or irradiated (12 Gy) HeLa cells stably expressing mock shRNA or shTIP60 were used for immunoprecipitation. Amounts of PARP-1, TIP60, and control GAPDH in input materials were detected by immunoblotting with the respective antibodies. (B) Anti-PAR antibody immunoprecipitates were subjected to an immunoblot analysis using an anti-PARP-1 antibody. Unirradiated or irradiated (12 Gy) HeLa cells stably expressing shTIP60 and reconstituted with either eTIP60 or eTIPM were used for immunoprecipitation. Input nuclear extracts immunoblotted with anti-PARP-1, an anti-HA antibody to detect eTIP60, and anti-GAPDH antibodies also are shown. (C) Immunopurified H2AX complex by sequential immunoprecipitation using anti-Flag and anti-HA antibodies. Immunoblots using anti-PAR and anti-H2AX antibodies are presented. (D) The H2AX complex immunopurified by an anti-Flag antibody was subjected to immunoblot analyses using anti-PAR, anti-PARP-1, anti-TIP60, anti-K5Ac H2AX, and anti-H2AX antibodies. HeLa cells, in which the endogenous H2AX was knocked down, were reconstituted with pOZ-C eH2AX WT or K5R (9). Cells were irradiated (12 Gy) before harvest. (E) Immunopurified H2AX complexes by anti-Flag antibody shown in panel D subsequently were immunoprecipitated using the anti-PAR antibody and subjected to immunoblot analyses using anti-PARP-1, anti-PAR, and anti-TIP60 antibodies.