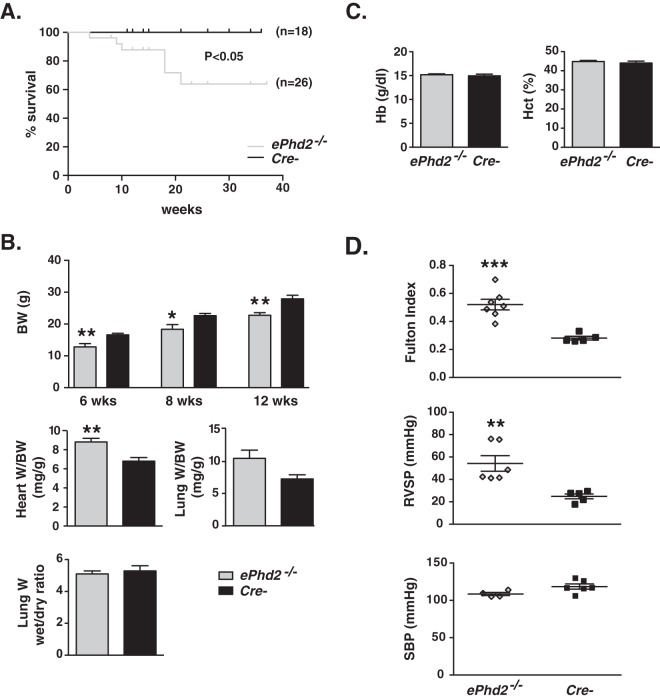
FIG 2.
Endothelial Phd2 inactivation results in premature mortality and pulmonary hypertension associated with right ventricular hypertrophy. (A) Shown are Kaplan-Meier survival curves for mutants and control mice. (B) The top panel shows body weights (BW) for ePhd2−/− mice and Cre− controls at 6, 8, and 12 weeks of age (n = 5 to 10). The middle panels depict ratios of heart or lung weight (W) to BW (heart, n = 8 or 9; lung, n = 3 or 4). The bottom panel shows the ratio of wet weight to dry weight for lungs from ePhd2−/− mutants and littermate controls (n = 5 or 6). (C) Hemoglobin (Hb) concentration and hematocrit (Hct) levels in ePhd2−/− mutants and controls (n = 5). Bars represent mean values ± SEM. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01. (D) Fulton index [(RV/(LV+S)] (n = 5 to 7), right ventricular systolic pressure (RVSP) (n = 5 or 6), and systolic blood pressure (SBP) in ePhd2−/− mice and Cre− controls (n = 4 to 6). Bars represent mean values ± SEM. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001.