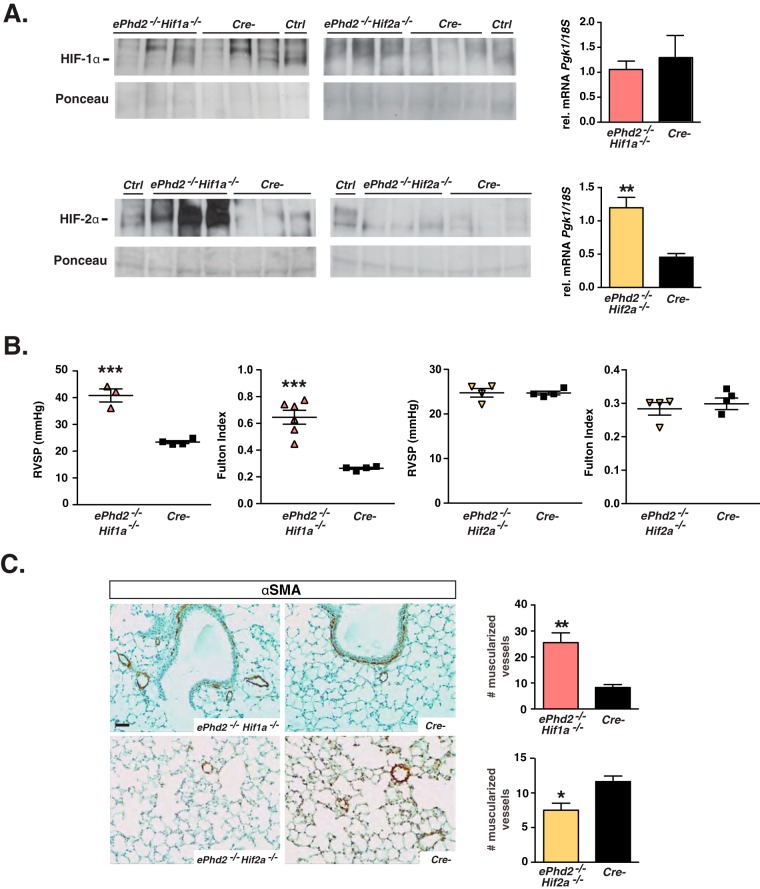
FIG 4.
Pulmonary hypertension in ePhd2−/− mice is dependent on HIF-2. (A) Shown are HIF-1α (top) and HIF-2α (bottom) protein levels as detected by immunoblot analysis of nuclear pulmonary extracts from ePhd2−/−Hif1a−/− mice, ePhd2−/− Hif2a−/− mice, and their Cre− littermate controls. Nuclear protein extracts from the kidney or liver of a PHI-treated mouse were used as positive controls (Ctrl). Ponceau staining was used to assess for equal protein loading. The graphs depict Pgk1 transcript levels in lungs from ePhd2−/− Hif1a−/− (n = 6) and ePhd2−/− Hif2a−/− (n = 5) mice. (B) RVSP and Fulton index in ePhd2−/− Hif1a−/− and ePhd2−/− Hif2a−/− mice. (C) Representative images of lungs stained for αSMA and quantification of muscularized vessels expressed as number/10 HPF in ePhd2−/− Hif1a−/−, ePhd2−/− Hif2a−/−, and control mice. Bars represent mean values ± SEM. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001. Scale bar, 50 μm.