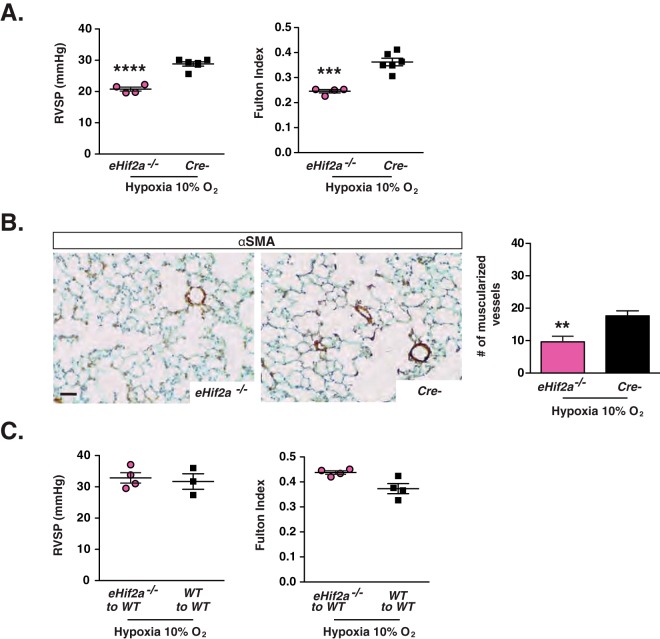
FIG 5.
Inactivation of endothelial Hif2a protects from the development of hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension. (A) Shown are RVSP and Fulton index measurements performed for eHif2a−/− and Cre− mice following chronic normobaric hypoxia (10% O2 for 4 weeks) (n = 4 to 6). (B) Representative images of lungs stained for αSMA, with the graph depicting muscularized vessel number/10 HPF in eHif2a−/− and Cre− mice following chronic hypoxic exposure (10% O2 for 4 weeks) (n = 4 to 6). (C) RVSP (n = 3 or 4) and Fulton index (n = 4) in transplanted WT mice subjected to chronic normobaric hypoxia (10% O2 for 4 weeks). eHif2a−/− to WT, WT mice transplanted with bone marrow cells from eHif2a−/− mutants; WT to WT, WT mice transplanted with bone marrow cells from WT mice. Bars represent mean values ± SEM. **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001. Scale bar, 50 μm.