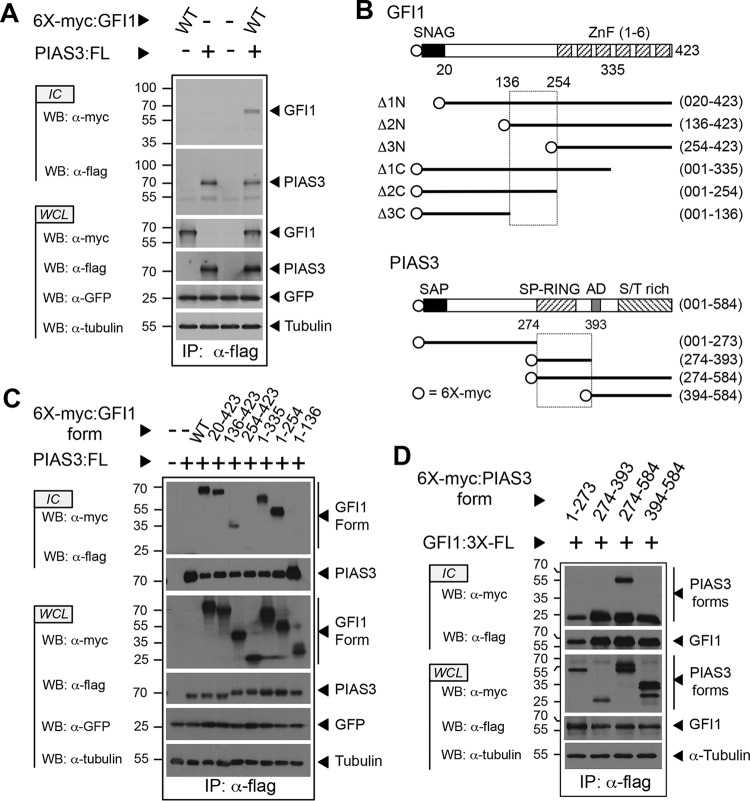
FIG 1.
The C-terminal half of the GFI1 linker binds the PIAS3 SP-RING domain. (A) PIAS3 binds GFI1. Myc-tagged GFI1 and Flag-tagged PIAS3 were expressed as shown. PIAS3 was immunopurified from whole-cell lysates (WCL), and coprecipitation of GFI1 was determined by immunoblot (Western blotting [WB]) analysis of immune complexes (IC). Green fluorescent protein (GFP) and tubulin were employed as controls for transfection efficiency and gel loading, respectively. (B) Structures of GFI1 and PIAS3 derivatives employed in the experiments shown in panels C and D. SNAG and ZnF regions are shown for GFI1. SAP, SP-RING, AD, and S/T-rich domains are shown for PIAS3. Amino acid residues corresponding to fragment boundaries are indicated in parentheses. Hatched boxes represent regions forming the GFI1-PIAS3 binding interface. Open circles indicate the 6×myc tag. (C and D) Mapping the GFI1-PIAS3 binding interface. PIAS3 and GFI1 forms, with accompanying epitope tags, were expressed as shown. Coprecipitating GFI1 (C) and PIAS3 (D) forms were identified by Western blotting. WT, wild type; FL, Flag epitope tag; IP, immunoprecipitation.