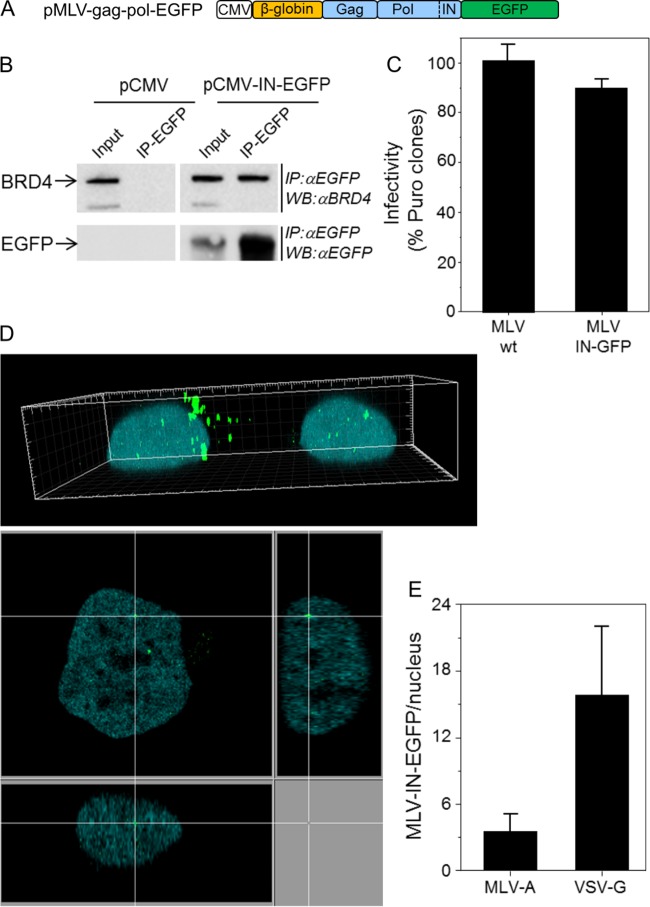
FIG 2.
MLV-IN-EGFP visualization system. (A) Schematic representation of the plasmid used to produce MLV-IN-EGFP particles. The construct was prepared as follows. The 3′-terminal end of MLV pol was amplified with primers MLV pol 5′ (GATCCTCGAGCTATAGAAAATTCATCACCC) and MLV pol 3′ (GATCAGATCTCCGGGGGCCTCGCGGGTTAAC) and with the phCMV-intron-gag-pol plasmid (a gift from François-Loïc Cosset) as the template DNA and cloned into the BglII site of plasmid pEGFP-N1 (Clontech). Next, a SnaBI-XmaI fragment encompassing the β-globin intron and MLV gag-pol from phCMV-intron-gag-pol was cloned into the SnaBI and XmaI sites of pEGFP-N1 containing the 3′ end of MLV pol. (B) HEK 293T cells transfected with plasmid pMLV-gag-pol-EGFP or control plasmid pCMV were immunoprecipitated (IP) with anti-EGFP antibodies (IP-EGFP) and analyzed by Western blotting with anti-BRD4 antibodies (Bethyl Laboratories, Inc.) (top) or anti-EGFP antibodies (bottom). Crude lysates (input) were loaded as controls. (C) MLV-IN-EGFP viral supernatants were produced by transfecting 5 × 106 HEK 293T cells with 20 μg of pBabe-Puro, 10 μg of pMLV-gag-pol-EGFP (or phCMV-intron-gag-pol), and 5 μg of pVSV-G with the polyethylenimine reagent. Supernatants were collected after 48 h and filtered through a 0.45-μm-pore-size filter. The infectivity of MLV-IN-EGFP was measured by counting the HeLa colonies resistant to puromycin 2 weeks postinfection with 2.87 reverse transcriptase units (RTU; measured by PCR-enhanced reverse transcriptase (PERT) assay [3]) and approximately corresponding to a multiplicity of infection of 1. wt, wild type. (D) HeLa cells expressing H2B-CFP and infected with MLV-IN-EGFP (2.87 RTU) in a 3D image (top) and a derived confocal section (bottom). (E) Numbers of MLV-IN-EGFP complexes in the nuclei of HeLa cells at 24 h postinfection. MLV-A and VSV-G indicate the envelopes used to produce MLV-IN-EGFP viral particles.