FIG 3.
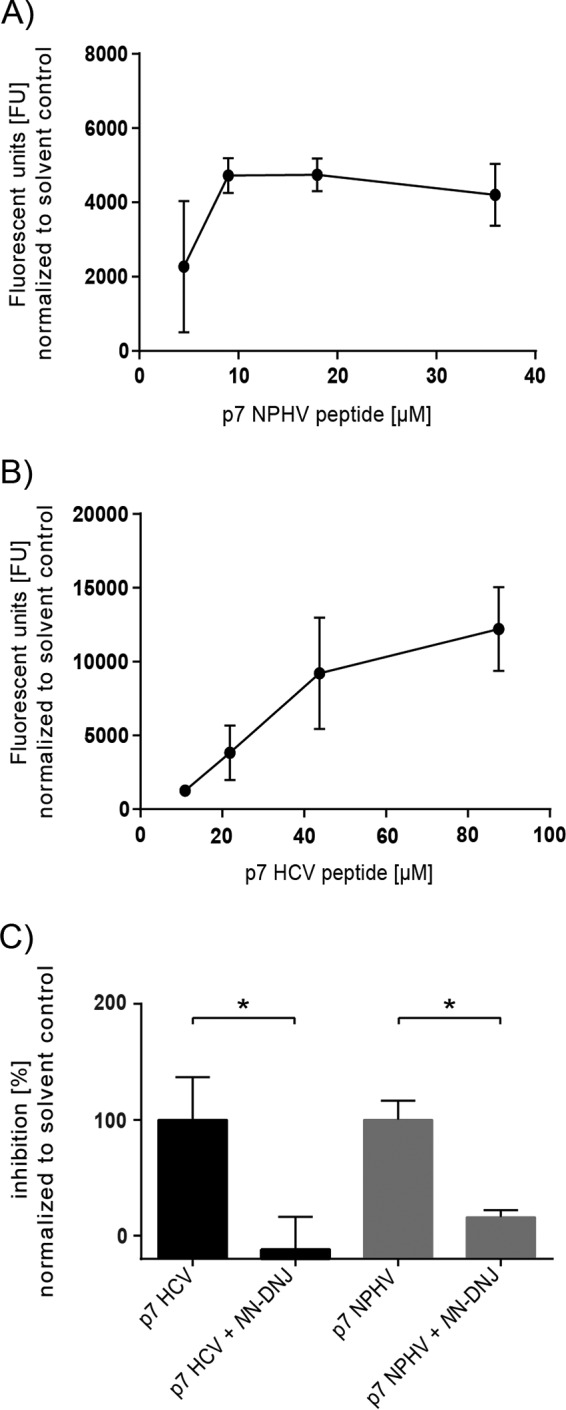
Evaluation of the NPHV p7 ion channel activity in a liposome permeability assay. The HCV and NPHV p7 peptides were chemically synthesized and used for subsequent liposome permeability assays. P7 peptides originating from the NPHV isolate H14 (A) and HCV isolate JFH-1 (B) were reconstituted in DMSO. Different concentrations of peptide were added to 50 μM carboxyfluorescein-loaded liposomes, and the fluorescence units (FU) were determined as an indicator of peptide-induced membrane permeability (activity). Liposomes supplemented with 1% (vol/vol) DMSO were used as solvent control. Three independent experiments in duplicate wells were conducted, and mean values ± standard deviations (SD) are depicted. (C) Inhibition assays with NN-DNJ were conducted. Therefore, liposomes contained 2% (vol/vol) DMSO with or without 40 μM NN-DNJ, these being the respective background levels for drug-free and drug-treated wells. Concentrations of 9 μM NPHV p7 peptide and 44 μM JFH-1 p7 peptide were used. Peptides with or without inhibitor were incubated for 20 min at RT prior to addition to the gain-adjusted plate on ice. Three independent experiments in duplicate wells were conducted. Depicted are the mean values + SD normalized to the respective solvent control. The percentage of inhibition was calculated by normalizing to the DMSO control without inhibitor. Statistical analysis was conducted by Welch's corrected unpaired t test. P values of <0.05 (*) were considered statistically significant.
