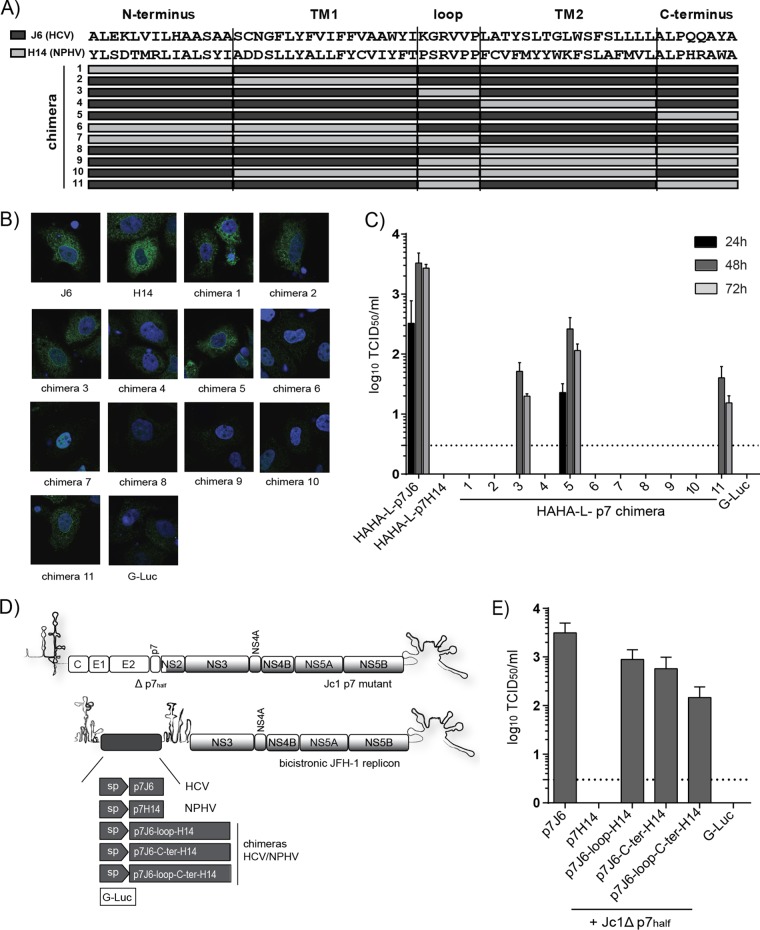
FIG 5.
Construction of HCV/NPHV p7 chimeras in a trans-complementation system. (A) Eleven distinct HCV/NPHV p7 chimeras were constructed by dividing p7 into 5 parts (N terminus, transmembrane helix 1 [TM1], loop, transmembrane helix 2 [TM2], and C terminus). The HCV isolate J6 and the NPHV isolate H14 were utilized as templates, and their respective amino acid sequences are depicted. Amino acid sequences originating from H14 are shown as light gray bars, whereas amino acids originating from J6 are shown as dark gray bars. P7 chimeras were cloned into the bicistronic helper replicon, including a signal peptide, a HAHA tag, and a short linker (see Fig. 4A). Constructed bicistronic helper replicons were transfected into Huh-7.5[C][E1E2][NS2]J6 by electroporation. (B) Cells were fixed 48 h posttransfection, and immunofluorescence analysis by staining for anti-HA and DAPI was performed. Shown are the respective merge pictures with the cell nuclei in blue and the anti-HA staining in green. Pictures were taken using a lens with a magnification of ×100. (D) Jc1 Δp7half was cotransfected into Huh-7.5 cells with in vitro-transcribed bicistronic JFH-1 helper replicons encoding a signal peptide (sp) downstream of p7J6, p7H14, p7J6-loop-H14, p7J6-C-ter-H14, and p7J6-loop-C-terH14 in the first cistron as well as a G-Luc. (E) Viral titers in supernatants 48 h posttransfection were determined by TCID50, and the means from three independent experiments are depicted as log10 TCID50 + SD.