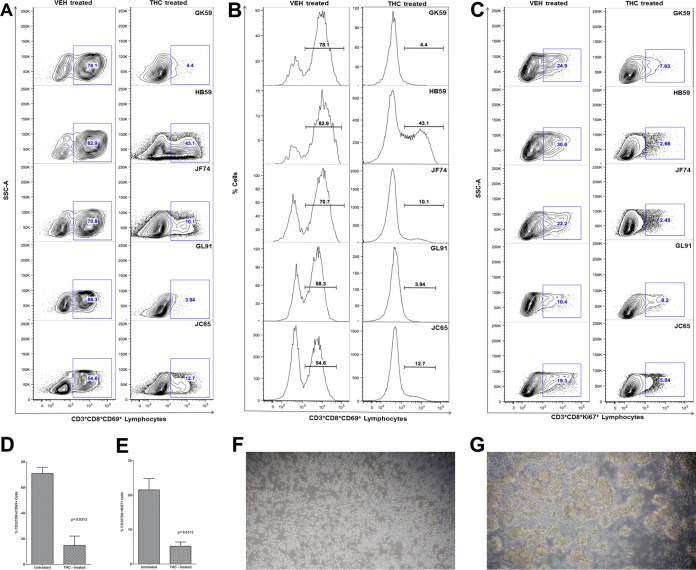
FIG 8.
THC inhibits CD8+ T-cell activation in vitro. THC-treated CD8+ T cells show significantly reduced expression of the lymphocyte activation marker CD69 (A and B) and proliferation marker Ki67 (C). Note the significantly reduced percentage of CD3+ CD8+ CD69+ and CD3+ CD8+ Ki67+ cells in all five animals 24 h after in vitro activation with PMA-ionomycin. Mean percentages of CD8+ CD69+ (D) and CD8+ Ki67+ (E) are significantly lower in THC-treated than in vehicle (VEH)-treated cells. THC-mediated inhibition of in vitro CD8+ T-cell activation (A and B) and proliferation (C) in response to PMA-ionomycin stimulation is evidenced by the absence of cellular clumps (F) compared to cells treated with vehicle (DMSO) (G). The error bars represent standard errors of the means of fold changes within each group.