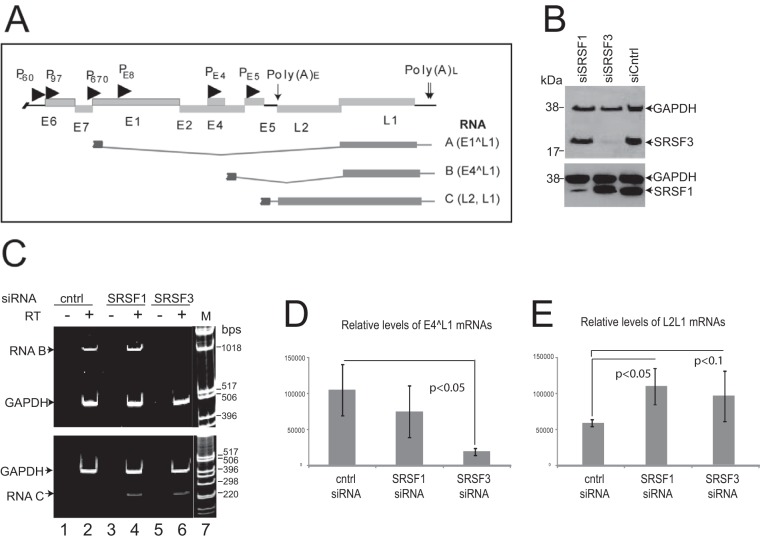
FIG 6.
SRSF3 controls levels of the E4^L1 mRNA. (A) Schematic diagram of the HPV16 genome. Open reading frames are represented with light gray boxes with the gene names beneath. Promoters are indicated with arrowheads. Polyadenylation sites are indicated with downward arrows [Poly(A)E/L]. The major late mRNA splicing events with the open reading frames (dark gray boxes), and introns (dark gray lines) are indicated below the genome map. Each mRNA is shown truncated at the 5′ end to indicate the presence of several possible initiation sites for the transcription of these mRNAs (10). The open reading frames in each mRNA are indicated on the right-hand side. (B) Western blot analysis of levels of SRSF1 and SRSF3 in NIKS16 cells following siRNA knockdown. siSRSF1, siRNA against SRSF1; siSRSF3, siRNA against SRSF3; siCntrl, control siRNA. GAPDH was detected as a protein loading control. (C) RT-PCR detection of HPV late mRNAs type B (upper gel) or type C (lower gel) in cDNA synthesized from RNA isolated from the same cell populations analyzed in panel B. Cntrl, control siRNA; SRSF1, siRNA against SRSF1; SRSF3, siRNA against SRSF3; RT, reverse transcriptase; M, 1-kb DNA marker ladder. GAPDH was amplified as an internal control for RNA concentrations. (D) Relative levels of E4^L1 spliced mRNA B compared to GAPDH mRNA determined by qPCR. The means and standard deviations from three separate experiments are shown. (E) Relative levels of unspliced L2L1 mRNAs compared to GAPDH mRNA, as determined by qPCR. The means and standard deviations from three separate experiments are shown. P values were calculated using a Student t test.