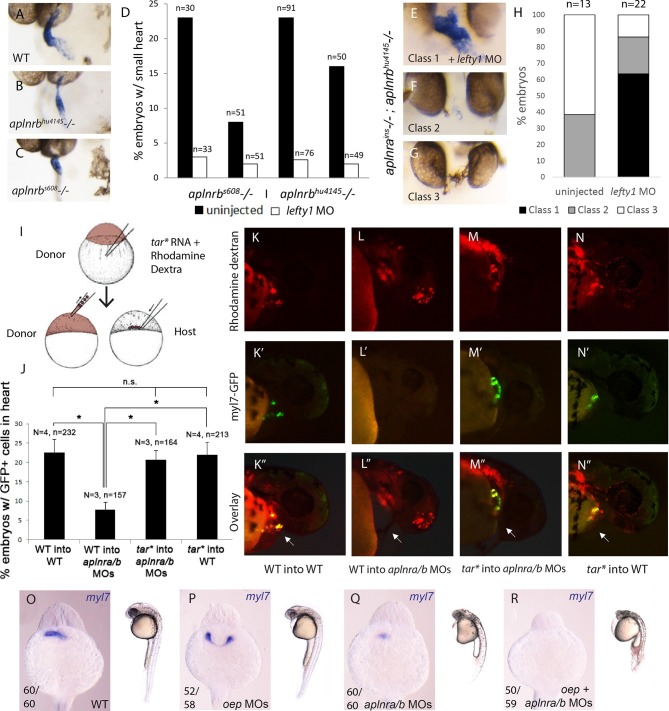
Figure 3. Elevation of Nodal signaling in aplnr mutant/morphant embryos rescues cardiogenesis.
(AC) myl7 WISH showing a representative heart phenotype at 48 hpf in a WT embryo (A) and two different aplnrb mutant alleles; hu4145 (B) and s608/grinch (C). Anterior is oriented towards the left. (D) Quantification of the number of embryos with a small heart at 48 hpf from individual clutches of embryos in which half were injected with lefty1 MO. Clutches were obtained from crosses of two different aplnrb heterozygous mutants (hu4145 and s608/grinch as indicated). (E–H) Classification of heart phenotype in aplnrains; aplnrbhu4145 double mutant embryos at 48 hpf when injected with lefty1 MO as compared to un-injected embryos. Severity of cardiac phenotypes was scored based on myl7 WISH (H). (I) Schematic displaying the transplantation of injected donor cells into the margin of host embryos. Contribution of transplanted cells to the heart is scored based on expression of the myl7:EGFP transgene in donor cells. (J–N”) Margin transplants of WT or tar* (activated Nodal receptor) overexpressing myl7:EGFP cells into WT or aplnra/b morphant embryos at 48 hpf. Arrow indicates the heart. Embryos are displayed from a lateral view with the anterior of the embryo towards the right. Data are represented as means ± SEM. *p<0.05, n.s. = not significant, Tukey’s Multiple Comparison test following significant (p<0.05) one way ANOVA. (O–-R) Gross morphology and myl7 expression at 24 hpf in WT (O), embryos injected with a sub-optimal dose of oep MOs (P), aplnra/b morphant embryos (Q) and aplnra/b/oep morphant embryos (R).