Figure 3. Dysregulated miRNA biogenesis in cancer.
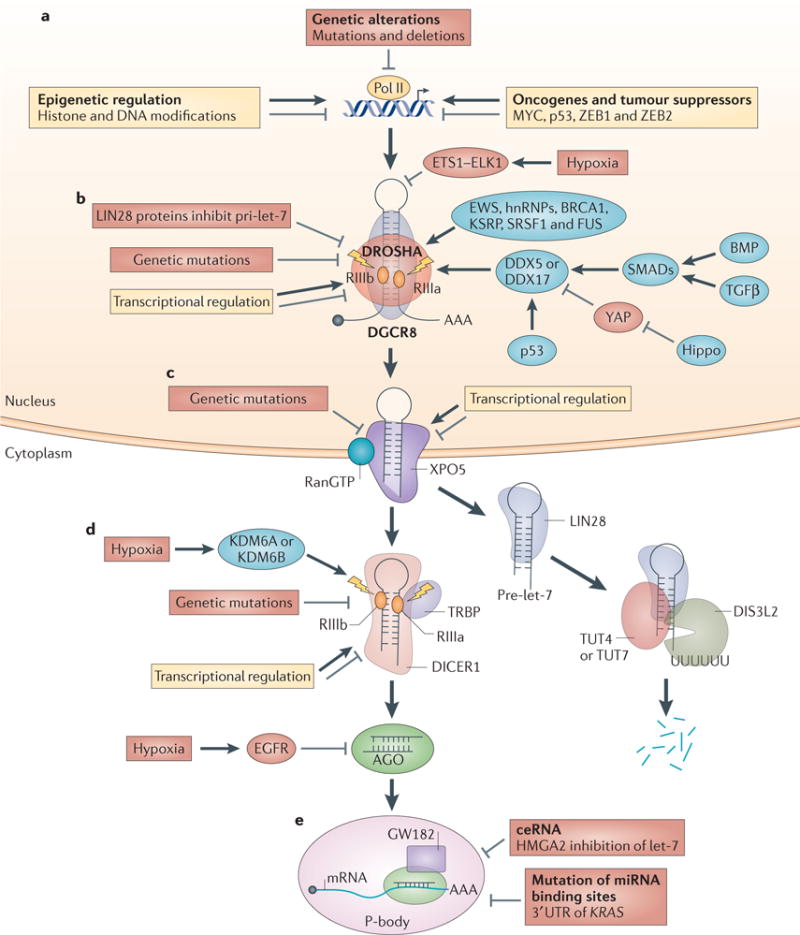
Aberrant microRNA (miRNA) biogenesis in cancer occurs at different steps during miRNA maturation. a | Genetic alterations, epigenetic modifications, oncogenes and tumour suppressors negatively or positively regulate primary miRNA (pri-miRNA) transcription in cancer. b | Pri-miRNA processing is regulated in the following ways: hypoxia, genetic mutations and transcriptional regulation control DROSHA and DiGeorge syndrome critical region 8 (DGCR8) expression in cancer; RNA-binding proteins such as DEAD box protein 5 (DDX5), DDX17 and BRCA1 modulate Microprocessor activity in cancer; cell signalling pathways such as Hippo and bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) regulate pri-miRNA processing; and LIN28 proteins selectively block the processing of pri-let-7. c | Genetic mutations in and transcriptional regulation of exportin 5 (XPO5) affect XPO5-mediated precursor miRNA (pre-miRNA) export in cancer. d | Pre-miRNA processing in cancer is regulated in the following ways: hypoxia, genetic mutations and transcriptional regulation modulate DICER1 expression and function to control pre-miRNA cleavage in cancer; LIN28 proteins selectively bind to pre-let-7 and recruit terminal uridylyltransferase 4 (TUT4), TUT7 and DIS3-like exonuclease 2 (DIS3L2) to degrade pre-let-7; and hypoxia-induced and epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-induced phosphorylation of Y393 of Argonaute 2 (AGO2) inhibits pre-miRNA processing. e | miRNA function is regulated in the following ways: competing endogenous RNA (ceRNA) inhibits miRNA function in cancer (high-mobility group AT-hook 2 (HMGA2) blocks let-7 function), as do mutations of miRNA-binding sites in non-small cell lung cancer (mutation of let-7-binding site in the 3′ untranslated region (UTR) of KRAS mRNA). hnRNP, heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein; KDM6, lysine-specific demethylase 6; KSRP, KH-type splicing regulatory protein; Pol II, RNA polymerase II; RIII, ribonuclease III; SRSF1, serine/arginine-rich splicing factor 1; TGFβ, transforming growth factor-β; TRBP, transactivation-responsive RNA-binding protein; YAP, Yes-associated protein; ZEB, zinc-finger E-box-binding homeobox.
