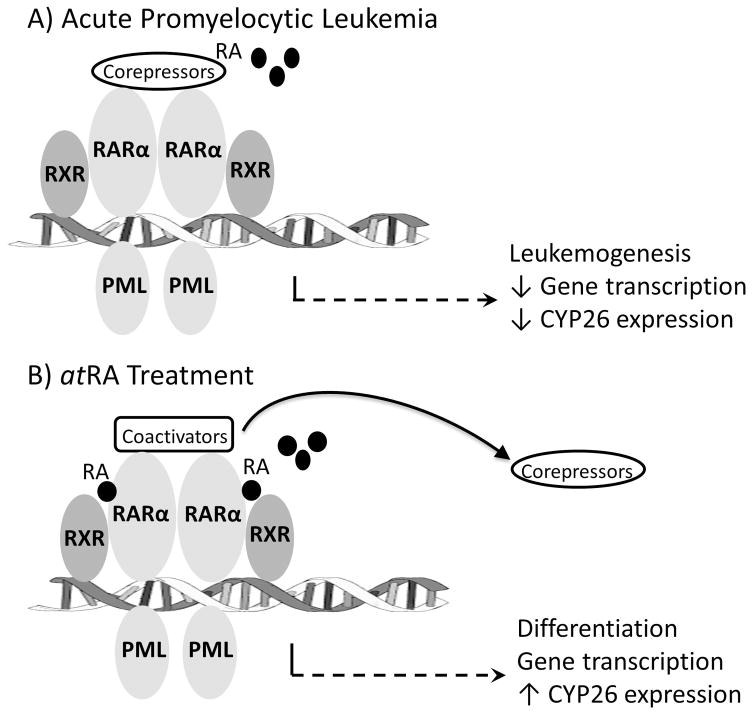
Figure 4. Retinoic acid and CYP26 signaling in acute promyelocytic leukemia.
In acute promyelocytic leukemia a chromosomal translocation forms the PML-RARα fusion protein which binds DNA as either a homodimer or multimeric complex with RXR. A) Physiological levels of the signaling molecule, RA, are insufficient to bind and promote release of corepressors from the complex which blocks gene transcription (including the gene for CYP26) and promotes leukemogenesis. B) Pharmacological levels of atRA bind the receptor, cause release of corepressors and recruit activators for gene transcription ultimately resulting in terminal myeloid differentiation.