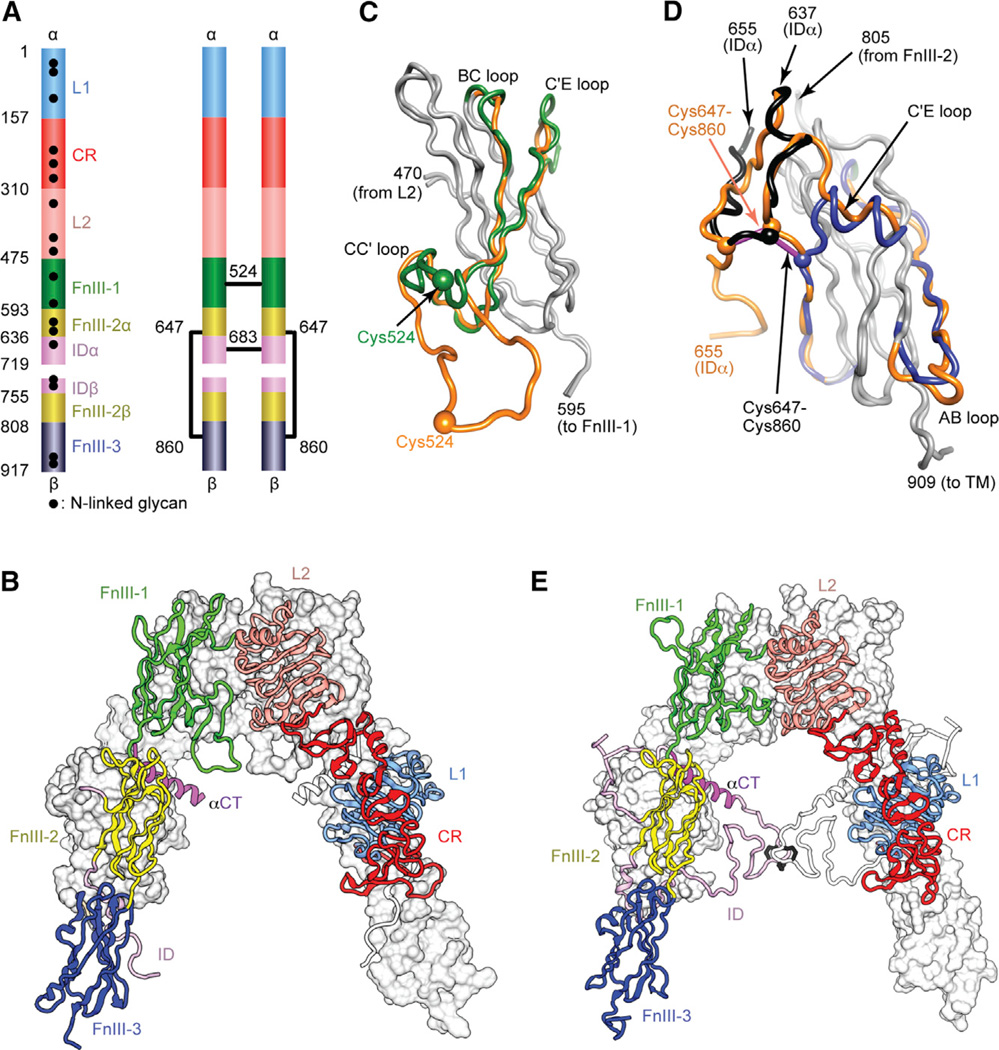
Figure 1. IR Ectodomain Structure.
(A) Domain structure of the αβ monomer and of the disulfide-linked (αβ)2 homodimer. Black lines denote inter-chain disulfide bonds. N-linked glycosylation sites are indicated for the monomer. (B) Inverted V-shaped arrangement of the domains within 3LOH. One monomer is in ribbon representation with domains labeled; the other is in molecular surface, apart from its ID which is in ribbon. (C and D) Revisions to FnIII-1 (C) and FnIII-3 (D). Regions of common residue register across 2DTG/ 3LOH and the revised structure are in gray; where the register differs, 2DTG/3LOH residues are in orange and those of the remodeled FnIII-1 in green, remodeled ID in black, and remodeled FnIII-3 in blue. Included in (D) is the ID segment 637–655 with the 647–860 intra-monomer α/β disulfide bond in purple rod representation.
(E) Revised IR ectodomain homodimer, represented as in (B).