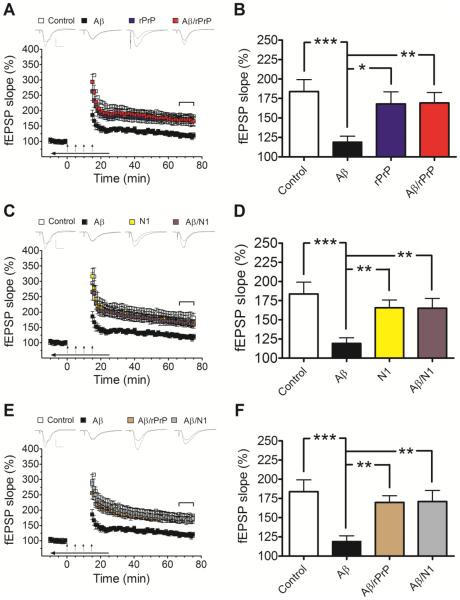
Fig. 2.
rPrP and the N1 fragment prevent Aβ-induced inhibition of LTP in mouse hippocampal slices. (A and C) Field potentials were recorded from the CA1 region of hippocampal slices in the presence or absence of Aβ oligomers alone or Aβ mixtures with rPrP (A) or N1 (C). These mixtures were prepared by adding rPrP or N1 to freshly disaggregated Aβ and incubating the samples for 3 h at 37 °C as described in Preparation of Aβ Oligomers for Preparation A. The concentration of Aβ in each case was 500 nM, and the concentration of rPrP or N1 was 100 nM (Aβ to rPrP or N1 molar ratio of 5:1). Controls are also included for rPrP and N1 alone. (B and D) Average fEPSP slopes during the last 10 minutes of field potential recordings derived from data shown in panels A and C, respectively. These data demonstrate strong protective effect of both rPrP and N1 against inhibition of LTP by Aβ oligomers (F(3, 39)= 5.112, p=0.0044; F(3, 39)=6.078, p=0.0017 for rPrP and N1, respectively). (E and F) A similar protective effect was observed when rPrP or N1 (both at a molar ratio to Aβ of 1:5) were added to Aβ oligomers that were preformed in the absence of these proteins (Preparation B described in Preparation of Aβ Oligomers) (F(3, 39)= 6.352, p=0.0013). The additives were bath applied for 10 minutes before establishing baseline; during tetanic stimulation (arrows); and for an additional 10 minutes after LTP induction (horizontal arrow bar). Representative traces of individual fEPSPs before and after LTP stimulation are shown on the top of panels A, C, and E (vertical bar: 1 mV; horizontal bar: 10 ms). The mean values are based on 10-12 independent experiments (one slice per animal per treatment), and error bars represent SEM. Statistical significance is expressed as *, **, and *** for p<0.05, p<0.01, and p<0.001, respectively. In control experiments it was verified that rPrP or N1 alone have no significant effect on LTP (blue and yellow bars in panels B and D, respectively).