Figure 1.
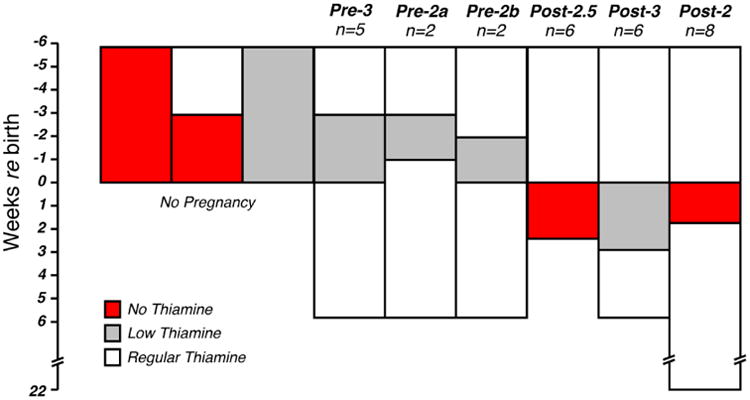
Schematic of the thiamine diet protocols. Mice were assigned to one of three groups: 1) Control animals, fed with regular chow (22 mg/kg thiamine); 2) Low-thiamine animals, fed with 0.2 mg/kg thiamine and 3) No-thiamine animals, fed with thiamine-free chow. Thiamine restriction was either applied prenatally (Pre) or postnatally (Post) for durations ranging from 2 to 6 wks. Females on a thiamine-free diet for ≥ 3 wks failed to become pregnant. On a low-thiamine diet, pregnancies went to full term if diet durations were ≤ 3 wks. Pups fed by mothers on a thiamine-free diet survived only if thiamine restriction was ≤ 18 days. Group sizes (n's) are indicated as number of ears evaluated.
