Figure 5.
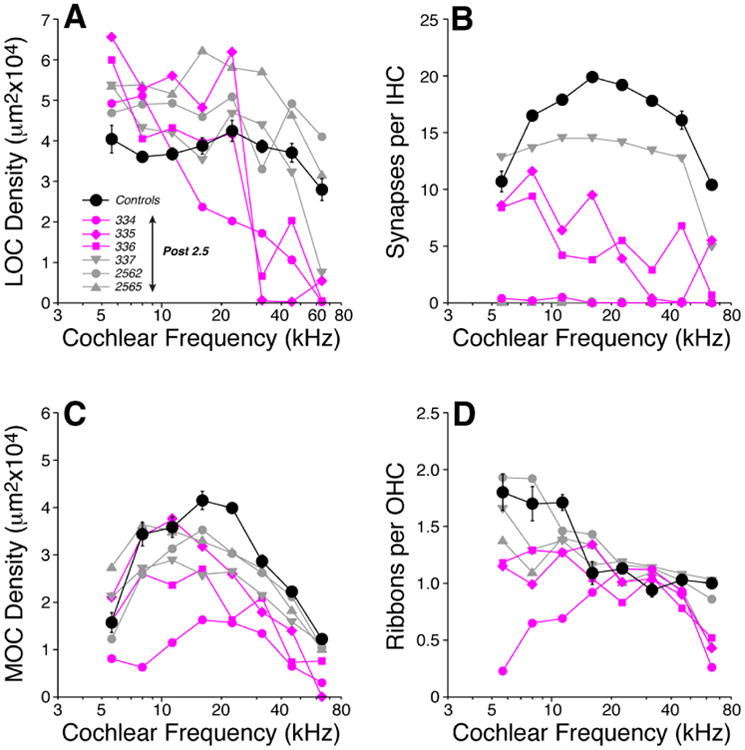
Mice with 18 days wks of postnatal thiamine deprivation (Post-2.5) are extremely weak and show profound changes in afferent and efferent innervation across all cochlear regions. LOC (A) and MOC (C) innervation densities, IHC synaptic counts (B) and OHC ribbon counts (D) in Post-2.5 ears are compared to age-matched (P18) Control mean values (± SEMs). Key in A applies to all panels: three of the thiamine-deprived ears with the most dramatic reduction in IHC synaptic counts are shown in color. IHC synaptic counts from two Post-2.5 mice (2562 and 2565) are missing from panel B because the background staining in the GluA2 channel was so high the signal from post-synaptic receptor patches was not interpretable.
