Figure 7.
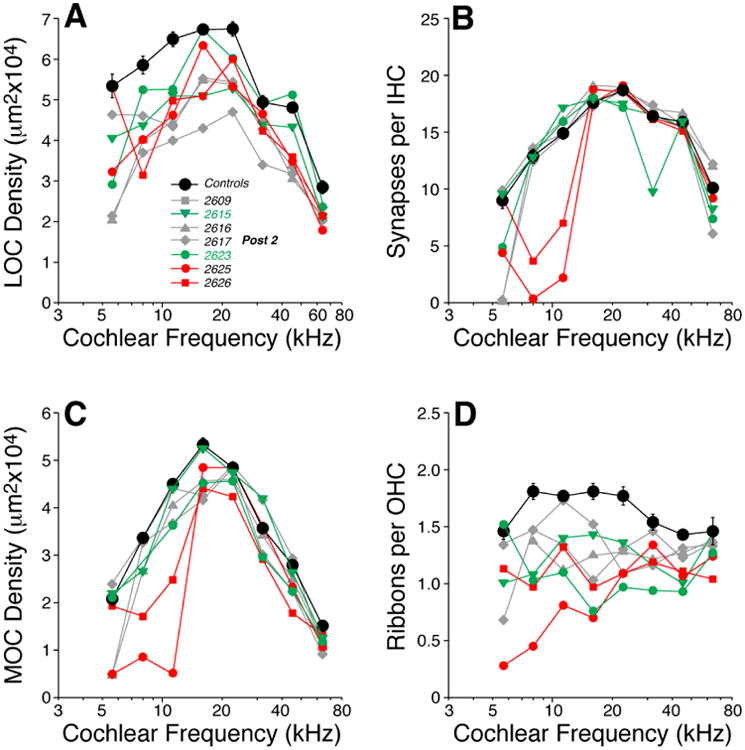
Two weeks of postnatal thiamine deprivation (Post-2) can lead to loss of afferent and efferent innervation, especially in the apical half of the cochlea. Panels A-D show the cochlear innervation abnormalities as seen at 22 wks. LOC (A) and MOC (C) innervation densities, IHC synaptic counts (B) and OHC ribbon counts (D) in individual Post-2 ears are compared to mean values from age-matched Control (± SEMs). Key in A applies to all panels: red symbols indicate cases with dramatic reduction of IHC synapses in the apex (B); green symbols indicate cases with exceptionally weak DPOAEs at high frequencies (Fig. 8).
