Figure 9.
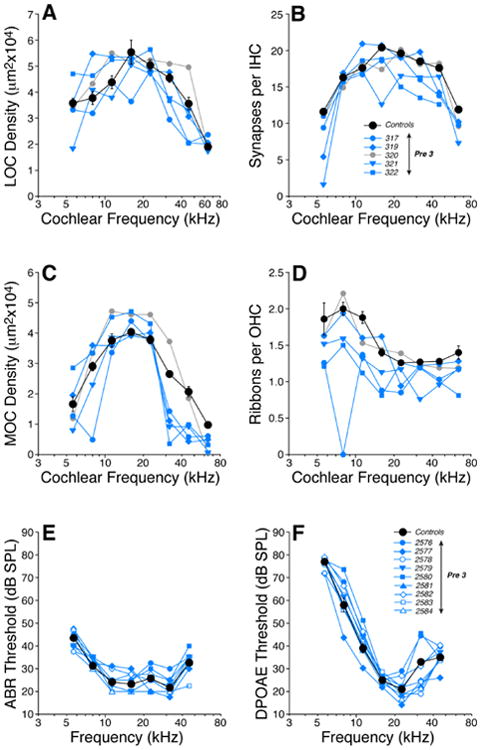
Prenatal thiamine restriction for 3 wks (Pre-3) leads to a moderate loss of afferent and efferent innervation without significant changes in cochlear thresholds. Panels A-D show the cochlear innervation abnormalities found in the offspring of mice fed on a low-thiamine chow during the last 3 wks of pregnancy (Pre-3 in Fig. 1). LOC (A) and MOC (C) innervation densities, inner hair cell synaptic counts (B) and outer hair cell ribbon counts (D) in each of the five Pre-3 mice are compared to mean values from age-matched Controls (± SEMs). Key in B applies to panels A-D: blue symbols are four cases with exceptionally low MOC densities in the cochlear base (C). Panels E-F show thresholds for ABRs (E) and DPOAEs (F) in Pre-3 mice compared to mean values for age-matched Controls (± SEMs). All measurements were done at 6 wks. Key in E also applies to F.
