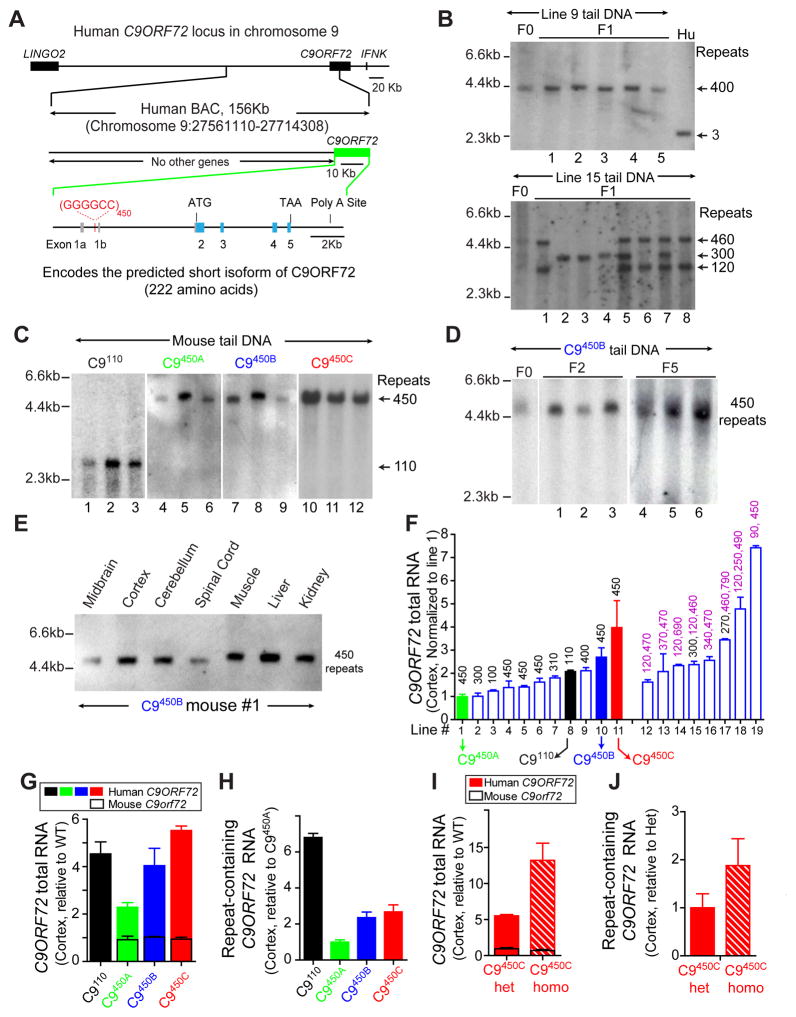
Figure 2. Generation of multiple BAC transgenic mouse lines expressing different levels of a human C9ORF72 transgene with 100 –700 GGGGCC repeats.
(A) Schematic of the human BAC containing 450 GGGGCC repeats in the first intron of a truncated human C9ORF72 gene. The coordinates of the BAC sequence on the University of California Santa Cruz Genome Browser (Hg19) are indicated. No other gene is on the BAC. (B–D) Genomic DNA blot analysis of tail DNA from (B) founder (F0) and F1 transgenic mice from lines 9 or 15 and DNA from human fibroblasts (Hu) with normal C9ORF72 alleles, (C) twelve different mice of lines 1, 8, 10 and 11 (re-designated C9450A, C9110, C9450B and C9450C, respectively), and (D) mice from F0, F2 and F5 generations in Line C9450B. (E) Repeat lengths determined by genomic DNA blotting using DNA from the CNS and peripheral tissues of a C9450B mouse. (F) Human C9ORF72 RNA in cortex of transgenic mice measured by qRT-PCR, normalized to C9450A mice. Numbers above bars are repeat lengths measured by genomic DNA blots. (G) Expression levels of total (mouse plus human) C9ORF72 RNAs in the cortex of C9110, C9450A, C9450B and C9450C mice normalized to the level of endogenous C9orf72 RNA. (H) Level of repeat-containing C9ORF72 RNA variants in the cortex measured by qRT-PCR and normalized to levels in C9450A mice. (I–J) Levels of (I) total C9ORF72 RNAs (human plus mouse) or (J) repeat-containing C9ORF72 RNA measured by qRT-PCR in the cortex of heterozygous and homozygous C9450C mice, normalized to C9orf72 levels in wild type littermates. Error bars represent s.e.m. from 3–5 biological replicates per group.
(See also Figure S3).