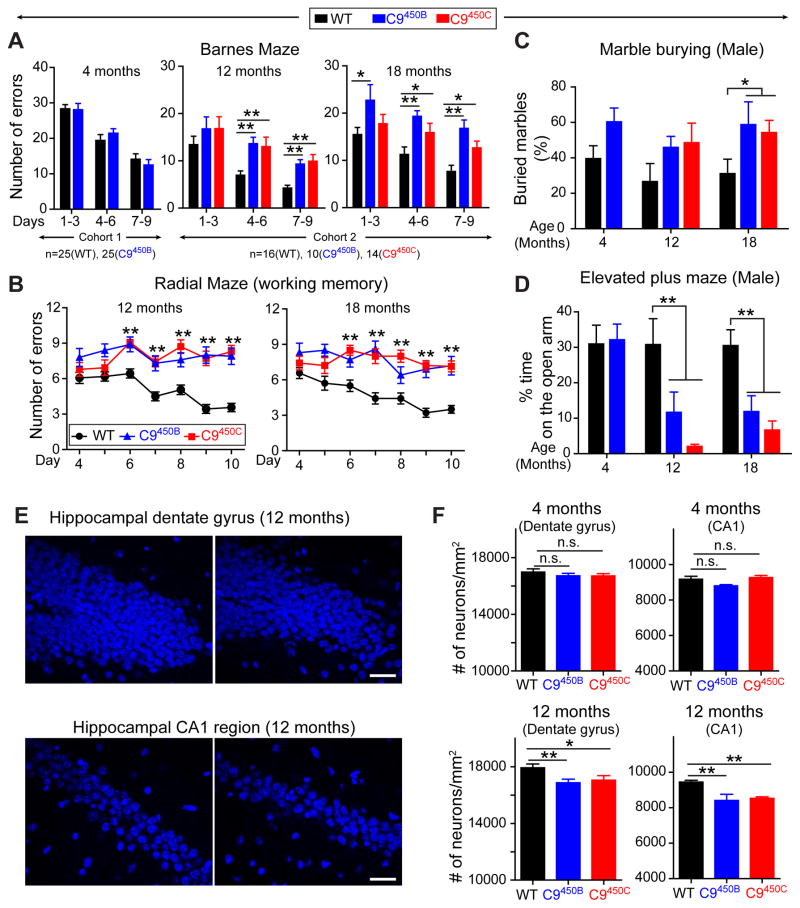
Figure 6. Age-dependent increased anxiety and impaired cognitive function in C9ORF72 mice with 450 repeats.
(A–B) Behavioral performances in WT, C9450B and C9450C mice at 4, 12 and 18 months of age [n=25 mice per group at 4 months and n=16 (WT), n=14 (C9450B) and n=10 (C9450C) at 12 and 18 months of age]. (A) Spatial learning and memory performance on a Barnes maze showing the number of errors in finding the escape chamber at days 1–3, 4–6 and 7–9. (B) Working memory performance on a radial maze showing errors per trial over 10 days of testing. (C–D) Anxiety-related behaviors in WT, C9450B and C9450C male mice at 4, 12 and 18 months of age [n=11 (WT) and n=13 (C9450B) at 4 months, and n=9 (WT), n=4 (C9450B) and n=7 (C9450C) at 12 and 18 months of age]. (C) Anxiety-related behavior determined by marble burying test showing the percent of marbles buried during a 20-minute trial, and (D) elevated plus maze showing the percent of time spent on the open arm. (E) Representative images and (F) quantification of DAPI-positive nuclei in the hippocampal dentate gyrus and CA1 region in 4 and 12 month old WT, C9450B and C9450C mice (n=4–5 per group). Error bars represent s.e.m, n.s., not significant, * p<0.05 and ** p<0.01 using one-way ANOVA.
(See also Figure S6 and S7).