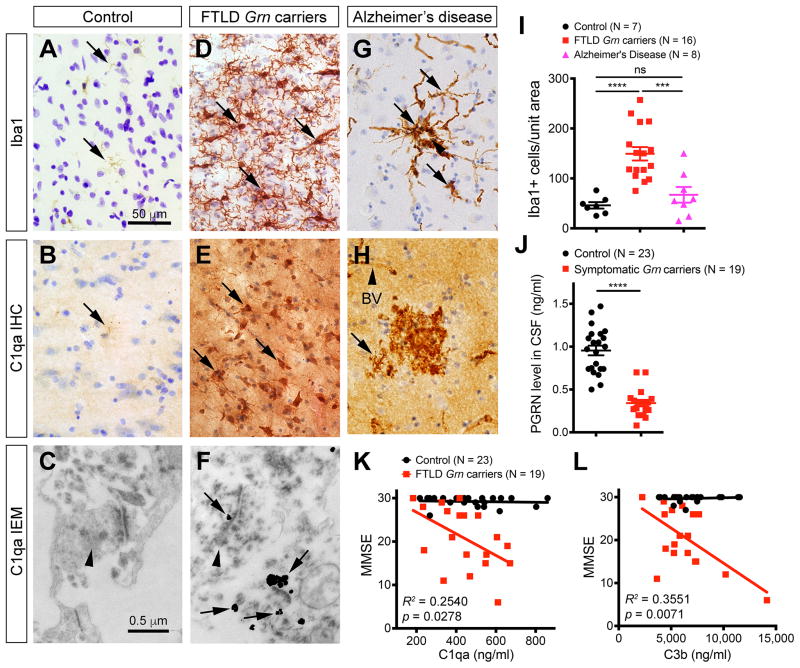
Figure 7. Microglial pathology and CSF complement levels in FTLD Grn mutation carriers.
(A–H) Immunostains of frontal cortex from control, FTLD Grn carriers and AD patients detect the presence of microglia and C1qa (A–B, D–E, G–H). In addition, immunogold EM detects the presence of C1qa deposits at the synapses in FTLD Grn mutation carriers (C, F). Arrows in A, B, D, E, G and H indicate microglia. Arrowhead in G indicates an amyloid plaque, and in H indicates a blood vessel (BV). Arrowheads in C and F indicate presynaptic terminals, and arrows in F indicate C1qa-positive immunogold particles in synapses. (I) Quantification of Iba-1+ microglia in the frontal cortex of controls (n = 7), FTLD Grn carriers (n = 16), and AD patients (n = 8). *** p < 0.005, **** p < 0.001, ns, not significant, Student’s t test. (J) Quantification of CSF PGRN levels in controls and FTLD GRN carriers. Student’s t test, **** indicates p < 0.0001. (K–L) ELISA assays for C1qa and C3b protein levels in the CSF of controls (n = 23) and FTLD Grn carriers (n = 19). Chi Square Goodness of Fit test to calculate R2 and p values. See also Figure S7, Tables S2 and Table S3.