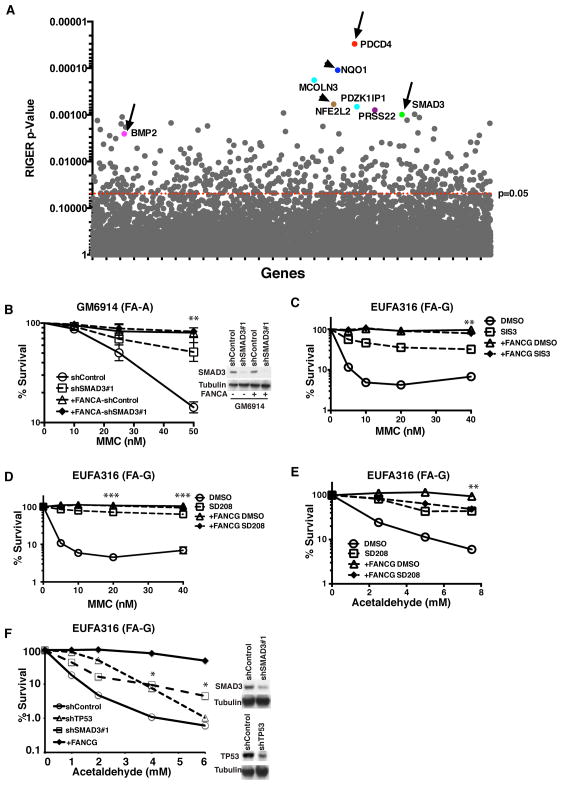
Figure 1. TGF-β Pathway Disruption Enhances Human FA Cellular Growth under Genotoxic Stress.
(A) RIGER P value analysis to identify top candidate genes in genome-wide screen. Top candidates are highlighted with different colors. Genes of the TGF-β pathway (BMP2, SMAD3, PDCD4) are pointed out by arrow. Genes involved in MMC metabolism (NQO1 and NFE2L2) are pointed out by arrowhead.
(B) Clonogenic survival of GM6914 (FA-A fibroblasts) and FANCA-corrected GM6914 cells after shRNA mediated knockdown of SMAD3. Cells were exposed MMC and cell survival was determined after 10–12 days in culture. The average of two independent experiments is presented. Immunoblot in the right panel shows SMAD3 knockdown efficiency in GM6914 cells.
(C,D) MMC sensitivity of EUFA316 (FA-G lymphoblasts) and FANCG-corrected EUFA316 cells incubated with or without 10μM SMAD3 inhibitor SIS3 or 10μM TGF-β inhibitor SD208. Cells were cultured in triplicates in presence of MMC and DMS0 or inhibitor for 5–6 days and survival was determined. Data are representative of 3 independent experiments.
(E) Acetaldehyde sensitivity of EUFA316 and FANCG-corrected EUFA316 cells incubated with or without 10μM SD208. Cells were exposed to acetaldehyde for 3 hours and survival was determined after culturing them for 5–6 days in presence of DMSO or SD208 in triplicates. The data are representative of 3 independent experiments.
(F) Acetaldehyde sensitivity of EUFA316 cells after shRNA mediated knockdown SMAD3 and TP53. Right panel shows the immunoblots of the lysates from EUFA316 cells showing shRNA-mediated knockdown of SMAD3 or p53.
Error bars represent mean ± s.e.m. *, p<0.05; **, p<0.01; ***, P<0.001. See also Figure S1.