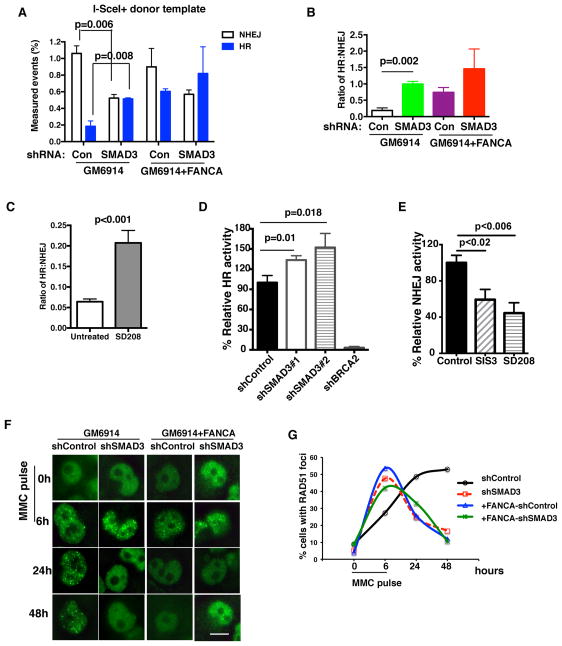
Figure 7. TGF-β Pathway Inhibition Increases HR and Decreases NHEJ activities in FA Cells.
(A, B) TGF-β pathway inhibition affects the choice of HR versus NHEJ pathways in repairing individual DNA breakpoints in FA cells. GM6914 cells (FA-A cells) or FANCA corrected GM6914 cells with shControl or shSMAD3 were used to generate traffic light reporter system, and then were infected with GFP-donor template and I-SceI lentivirus to generate DNA breakpoints. Quantification analysis of HR and NHEJ repair events is shown. (B) The ratio of HR to NHEJ activity based on the data in (A).
(C) SD208 mediated TGF-β pathway inhibition increases HR events and decreases NHEJ events. Quantification of HR and NHEJ repair events in GM6914 cells exposed to SD-208 for 72 hrs as detected by traffic light reporter assay described in (A).
(D) SMAD3 knockdown significantly increases HR efficiency. HR assay was measured in U2OS cells with DR-GFP reporter after transduction with lentivirus encoding indicated shRNAs. The representative of three independent experiments is presented.
(E) NHEJ reporter assay showing decreased NHEJ activity in U2OS cells after inhibition of the TGF-β pathway by small molecule inhibitors.
(F, G) TGF-β pathway inhibition promotes HR activity in FA cells. Representative images (F) and quantification (G) of RAD51 foci in MMC treated GM6914 (FA-A) cells or FANCA-corrected GM6914 cells with shRNA-mediated knockdown of SMAD3. Cells were exposed to 1μM MMC for 6h, and allowed to recover for 24h and 48h. RAD51 foci were then identified. One hundred cells were scored for RAD51 foci. (Scale bar: 20μm)
Error bars represent mean ± s.e.m. See also Figure S7.