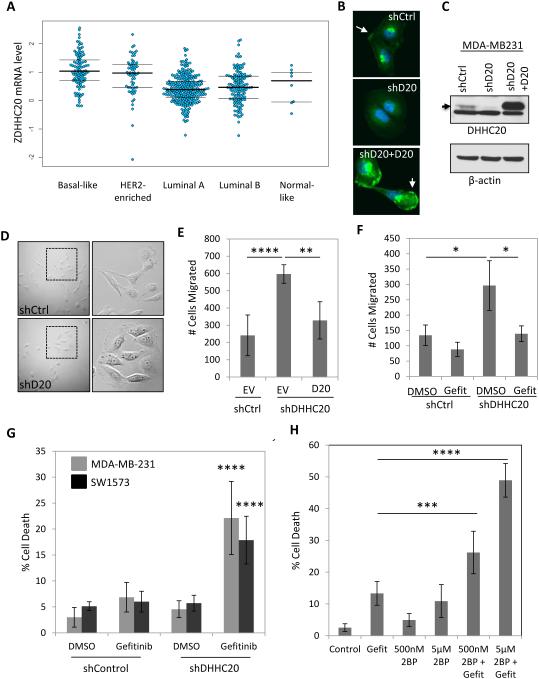
Figure 1. Silencing DHHC20 increases EGFR-dependent cell migration and enhances Gefitinib-induced cytotoxicity.
(A) DHHC20 mRNA expression is altered in human breast cancer subtypes. Global patterns of ZDHHC20 expression were identified in human breast invasive carcinoma in the TCGA database; Basal-like (n=98), HER2-enriched (n=58), Luminal A (n=230), Luminal B (n=125) and Normal-like (n=8). (B-C) DHHC20 expression measured by immunoblotting and immunofluorescence microscopy is inhibited by shRNA in MDA-MB-231 cells. Expression of shRNA resistant DHHC20 produces a product with the same molecular weight and cellular localization as the endogenous protein. (B) Immunofluorescence staining of DHHC20 (green) and DAPI (blue) show expression of DHHC20 at the plasma membrane (arrow) and perinuclear region. (C) Immunoblotting with a DHHC20 specific antibody shows inhibition of the DHHC20 band (arrow). (D) Silencing DHHC20 in MDA-MB-231 cells induces cell spreading with increased membrane ruffling. (E) Knockdown of DHHC20 increases chemotaxis towards FBS and this is rescued by expression of shRNA resistant DHHC20 (mean +/−StDev). (F) Increased chemotaxis of shDHHC20 MDA-MB-231 cells is inhibited by treatment with Gefitinib (10μM) (mean +/−StDev). (G) Gefitinib treatment (10 μM) increases cytotoxicity in DHHC20 silenced MDA-MB-231 (gray bars) and SW1573 (black bars) cells (mean +/−StDev). (H) Inhibiting palmitoylation with 2BP increases Gefitinib induced cytotoxicity. MDA-MB-231 cells were treated with 10μM Gefitinib alone or in combination with 500nM or 5μM 2BP (mean +/−StDev).