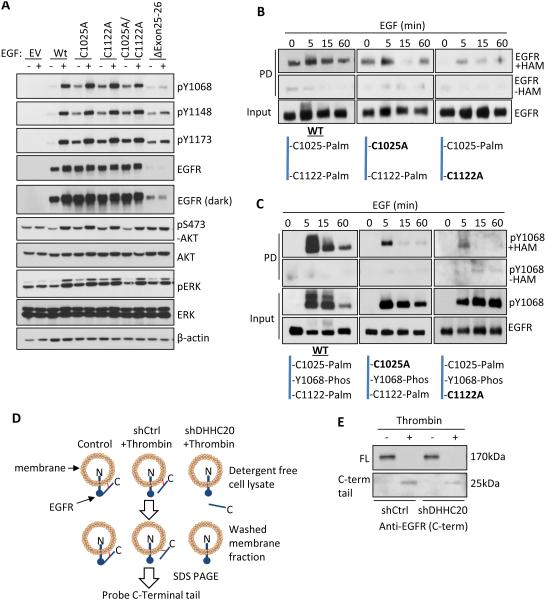
Figure 6. Palmitoylation regulates the activity of EGFR in response to EGF.
(A) Mutation of EGFR palmitoylated cysteine residues increases EGFR activation independent of EGF in NIH 3T3 cells compared to WT EGFR. (B) EGFR palmitoylation increases upon EGF (100ng/ml) stimulation in MDA-MB-231 cells. (C) Dually phosphorylated and palmitoylated EGFR and EGFR mutants C1025A and C1122A turns over more rapidly than total EGFR in response to EGF (100ng/ml). (D) Experimental strategy of the thrombin cleavage assay. (E) Palmitoylation pins the C-terminal tail of EGFR to the cell membrane. HEK293T cells transiently expressing EGFR-FLAG containing a thrombin cleavage site (LVPRGS) at Gly959 were lysed in the presence or absence of thrombin protease. The membrane fraction was isolated by centrifugation and EGFR was immunoprecipitated from the membrane fraction. The presence of membrane bound full length (170kDa) EGFR and the cleaved C-terminal tail (25kDa) was determined by SDS-PAGE.