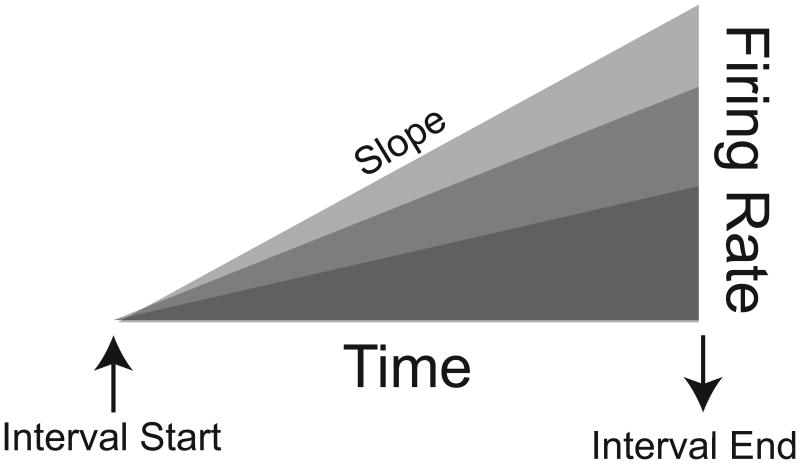
Figure 1.
Ramping activity. Neural activity increases after the start of a temporal interval, as indicated by a predictive stimulus or preparatory movement. Temporal expectation anticipating movement and/or reward grows over time and neural ramps accordingly. The slope of the ramp can also encode interval duration. Ramping activity can also decrease which would be the inverse of the pattern represented here, and can also have logarithmic features.