Fig. 7.
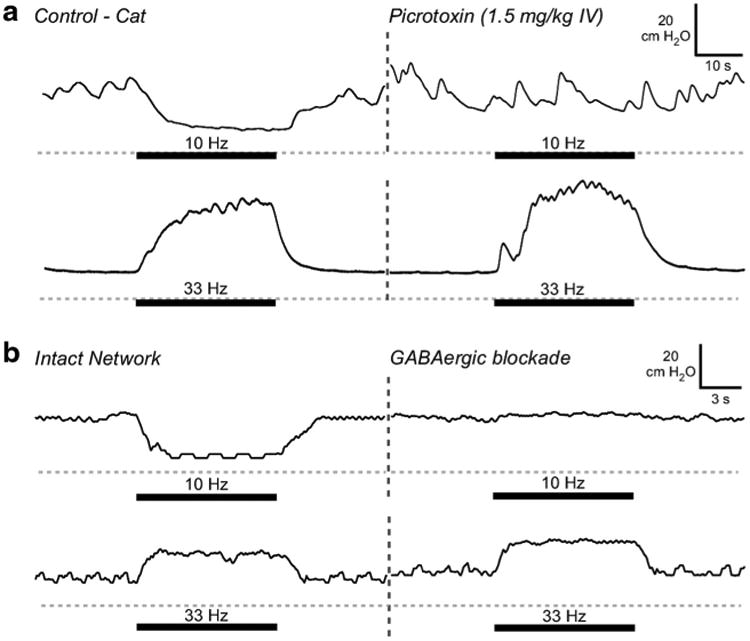
Effects of gabaergic blockade on response to pudendal afferent stimulation. a Bladder pressure traces from experiment in α-chloralose anesthetized adult cat (gray dashed line = 0 cmH2O) (McGee et al. 2014; McGee and Grill 2014). Thick bar indicates when stimulation was applied. Inhibition of bladder contractions by 10 Hz pudendal DGN afferent stimulation was eliminated following administration of the GABAA receptor antagonist picrotoxin. Stimulation-evoked bladder contractions were produced by 33 Hz stimulation before and after the administration of picrotoxin. b Simulated blockade of GABAergic inhibitory synapses in the model mimicked the effects of administration of picrotoxin. Pudendal afferent stimulation-evoked inhibition with 10 Hz was lost following blockade of model GABAergic synapses. Bladder contractions evoked by 33 Hz pudendal afferent stimulation were unaffected by the reduction in synaptic weight of inhibitory synapses in the neural network, consistent with experimental results (McGee et al. 2014)
