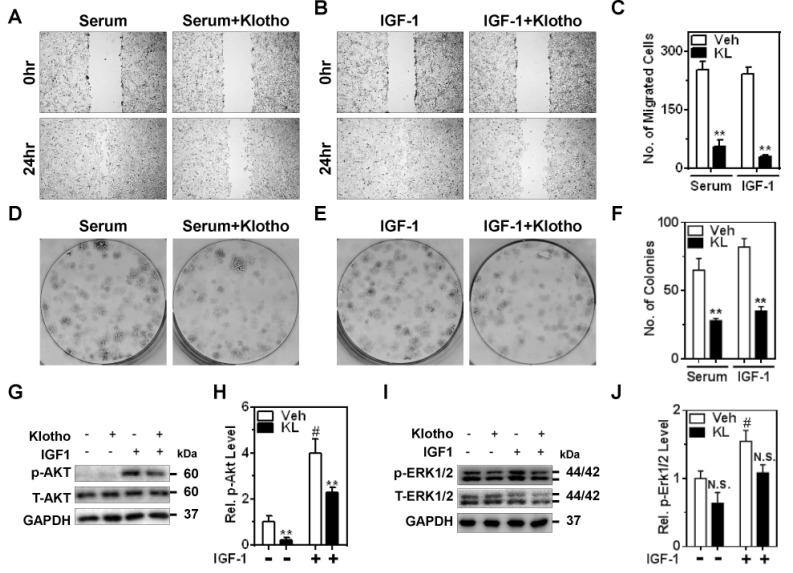
Fig. 2. Klotho suppresses serum growth factors and IGF-1-stimulated cell migration and proliferation of ccRCC via PI3K/Akt pathway.
(A and B) Caki1 cell migration was examined using wound-healing assay with the presence of mitomycin C (0.1 µg/ml). Serum (10% FBS) and IGF-1 (100 nM)-induced cell migration was inhibited by pretreatment of Klotho (KL; 1 nM) in Caki1. (C) Number (No.) of migrated cells in the wound area in panel A and B. **p<0.01 versus vehicle (Veh). (D and E) Effect of Klotho on serum and IGF-1-induced colony formation in Caki1 cells. (F) Quantitative analysis of colony formation assay from three independent experiments in panel D and E. **p<0.01 versus Veh (G and I) Representative immunoblotting of p-Akt and p-Erk1/2 by IGF-1R stimulation and Klotho effect. GAPDH was used for loading control. (H and J) Quantitative analysis from panel G and I, respectively (Rel.= elative). **p<0.01 versus Veh. #p<0.01 versus no IGF-1. N.S., not significant. Note; in panel J, p-values for Veh vs KL are 0.13 and 0.08 in control (no IGF-1) and IGF-1-treated groups, respectively.