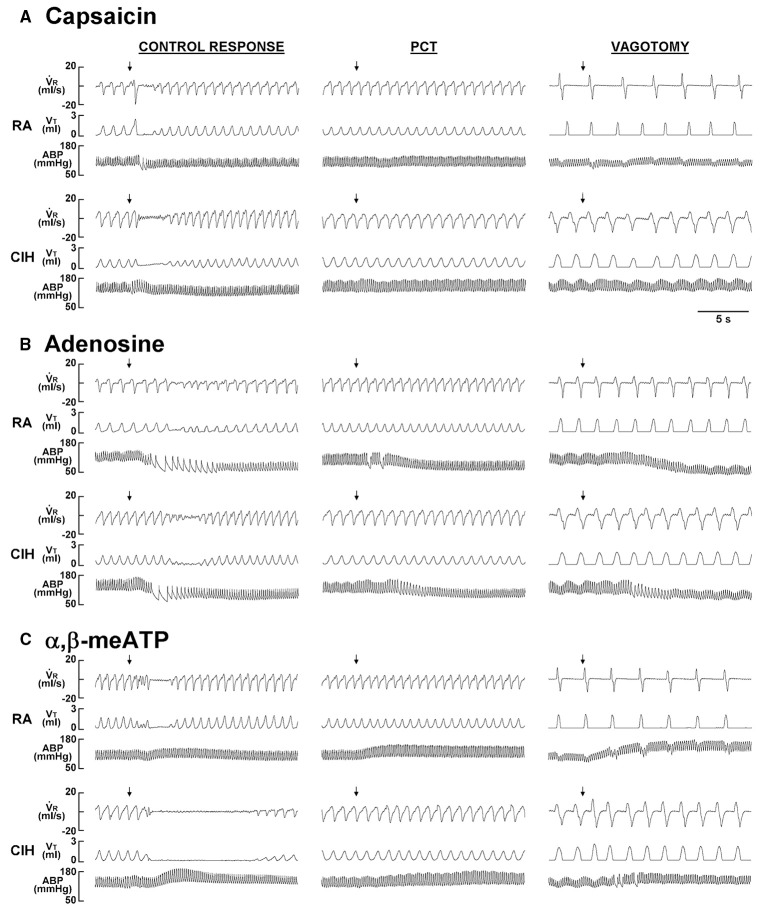
Figure 1.
Ventilatory responses to the intravenous injection of three types of stimulants in two rats after exposure to room air or chronic intermittent hypoxia. Duration of exposure to room air (RA) or chronic intermittent hypoxia (CIH) was 14 days. At 16 h after the last exposure, the animals' responses to capsaicin (1.0 μg/kg; A), adenosine (0.2 mg/kg; B), and α,β-methylene-ATP (α,β-meATP; 15 μg/kg; C) were measured in each rat under control conditions, after perivagal capsaicin treatment (PCT; 250 μg/ml), and then after bilateral cervical vagotomy. These drugs are stimulants of lung vagal C fibers and were injected into the jugular vein as a bolus (0.1 ml volume) as indicated by the arrows. The injection catheter had its tip close to the right atrium. Approximately 15 min elapsed between any two injections. VR, respiratory flow; VT, tidal volume; ABP, arterial blood pressure.