Figure 1.
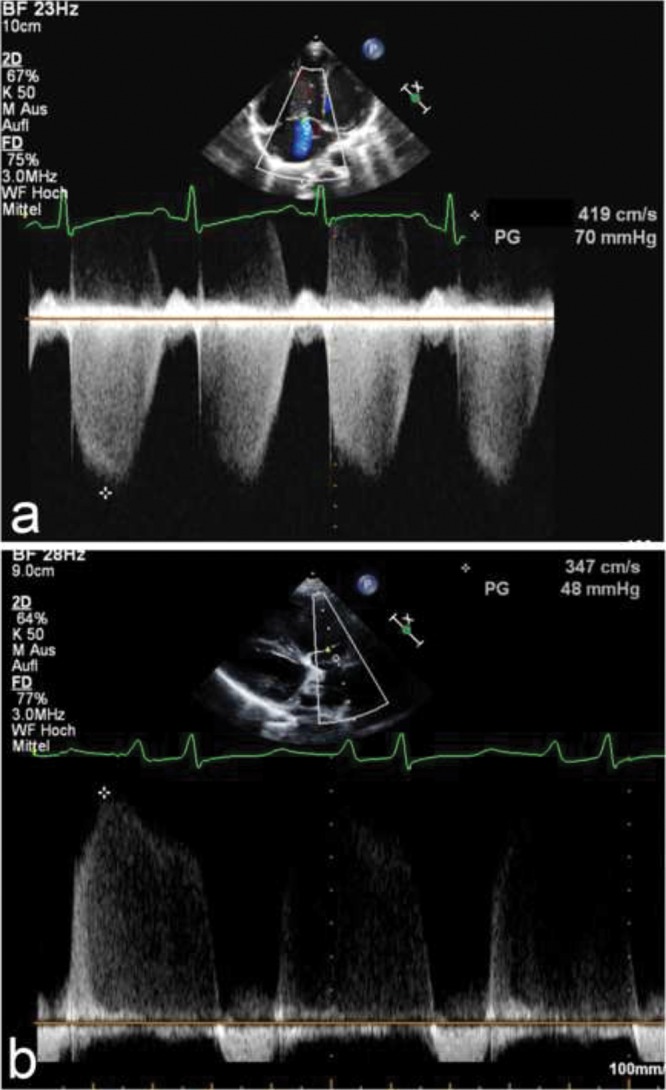
a, Apical 4-chamber view. Estimation of the systolic pulmonary artery pressure (PAP), by estimating the right ventricular systolic pressure by measurement of the velocity of the tricuspid regurgitation (TR) jet using continuous-wave (CW) Doppler. The dashed white line indicates CW Doppler cursor placement at the TR. The peak TR jet velocity is above 4 m/s, thus indicating an increased pressure gradient between the right ventricle and the right atrium (RA). This, added to an assumed RA pressure, estimates the systolic PAP. b, Parasternal short-axis view. Estimation of the mean PAP through CW Doppler of the pulmonary regurgitation (PR) jet. The dashed white line indicates CW Doppler cursor placement at the PR. The mean PAP is calculated as the PR gradient, with a markedly increased value of 48 mmHg compared to normal values (<25 mmHg). The end-diastolic regurgitant velocity is 2.5 m/s. When added to an assumed RA pressure of 10 mmHg, this estimates a pulmonary artery diastolic pressure of 35 mmHg.
