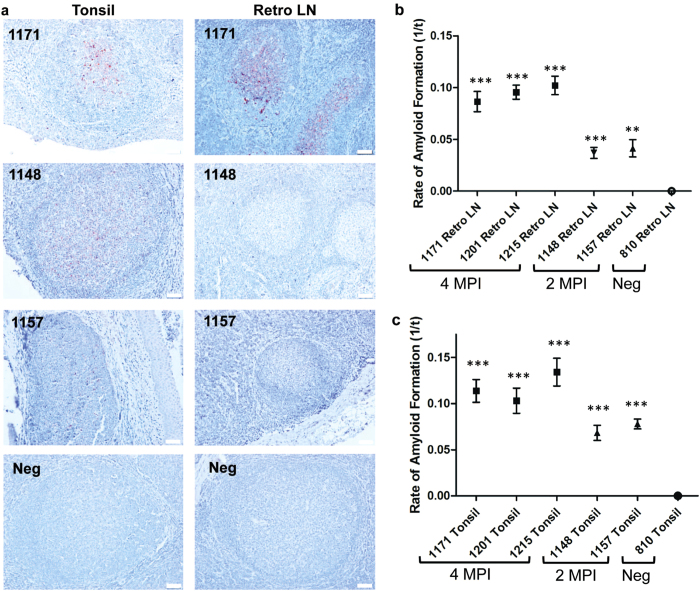
Figure 4. Analysis of FPE lymphoid tissues from subclinical CWD-infected WTD by RT-QuIC.
(a) Representative IHC of FPE lymphoid tissues from subclinical, CWD-infected WTD. Tissues collected at 4 MPI have increased density of PrPCWD staining when compared to 2 MPI tissues reflecting a greater prion accumulation over the disease course. The low-level of PrPCWD staining at 2 MPI reflects the early course of disease. RT-QuIC detected amyloid seeding activity in FPE samples that are IHC negative (1148 Retro LN). All IHC images are 200× magnification, measurement bars represent 50 μ m. (b) RT-QuIC of subclinical WTD retropharyngeal lymph nodes. All retropharyngeal lymph nodes from subclinical animals displayed significant amyloid seeding activity (means analyzed by one sample t-test; **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001) when compared with respective negative control tissues. Lymph nodes collected at 4 MPI had higher RT-QuIC amyloid formation rates than tissues collected at 2 MPI which is consistent with greater PrPCWD amyloid seeding activity. Each point represents the mean and SEM derived from eight replicates and in two separate experiments. All FPE samples are assayed at a 10−1 dilution. (c) RT-QuIC of subclinical WTD tonsils. All tonsils from subclinical animals displayed significant amyloid seeding activity (means analyzed by one sample t-test; ***p < 0.001) when compared with respective negative control tissues. Similar to the retropharyngeal lymph nodes in (b), tonsils collected at 4 MPI had higher RT-QuIC amyloid formation rates than tissues collected at 2 MPI which is consistent with greater PrPCWD amyloid seeding activity. Each point represents the mean and SEM derived from eight replicates and in two separate experiments. All FPE samples are assayed at a 10−1 dilution.