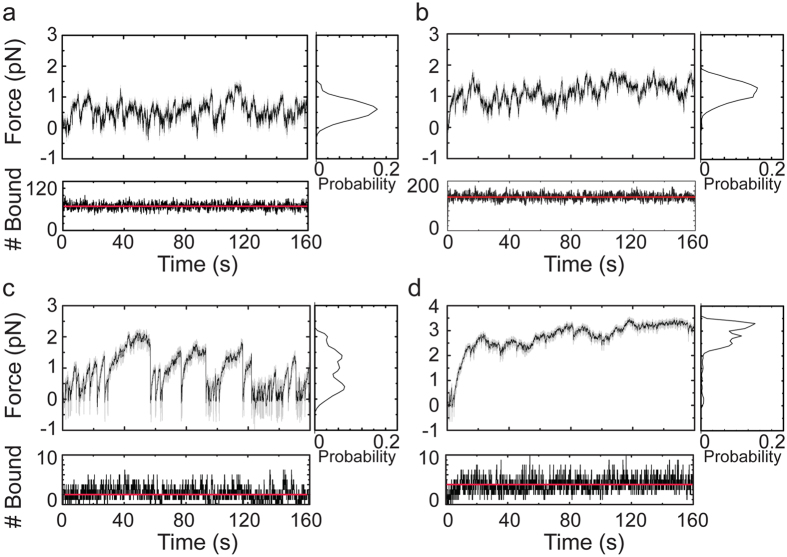
Figure 5. Simulated force developed on actin filaments by ensembles of Myo1c molecules on lipid and solid substrates.
(Large panels) Force on actin dumbbells pulled by Myo1c molecules dynamically attached to a diffusive surface at densities corresponding to average number (over 50 realizations) of actin-bound motors (a) N = 69.04 and (b) N = 123.61. Actin dumbbells pulled by Myo1c3IQ molecules rigidly anchored to a surface at densities corresponding to average number of actin-bound motors (c) N = 2.14 and (d) N = 3.56. Unfiltered (gray) and smoothed (black) force traces of the beads attached to the barbed-end of the actin filaments are shown. (Right subpanels, dashed lines) Probability histograms of the force are also shown. (Lower subpanels) Traces showing the number of Myo1c molecules bound to actin filament as a function of time.