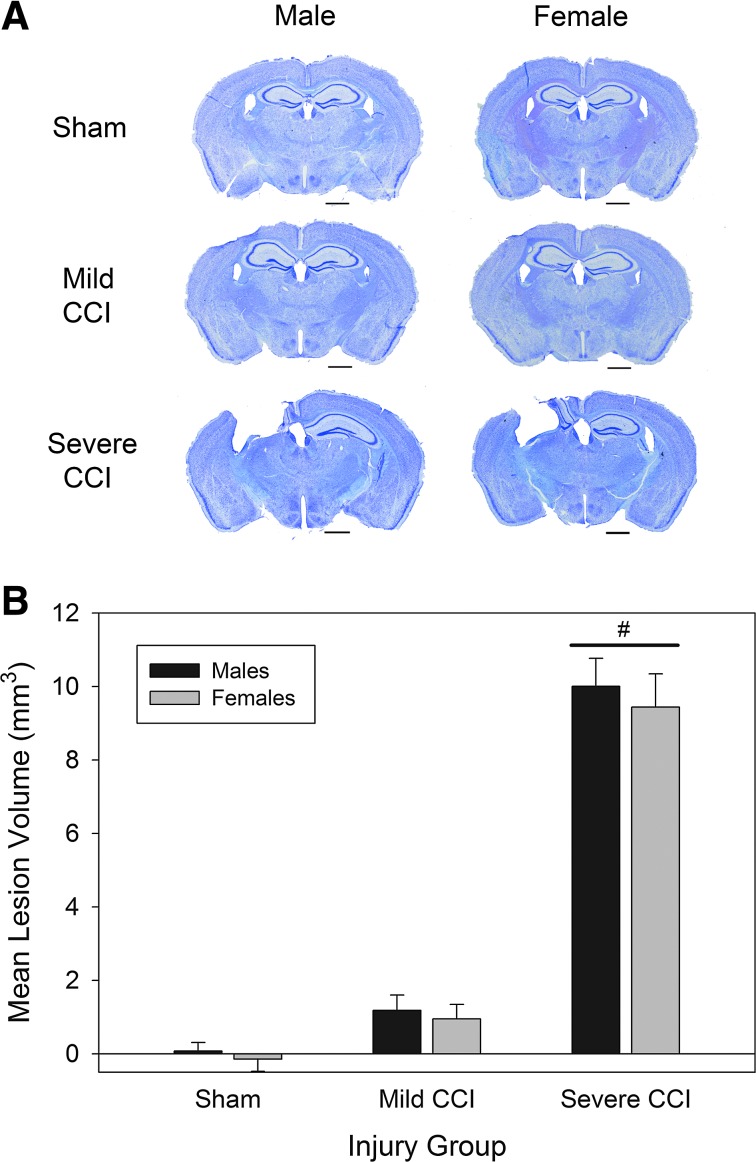
FIG. 1.
Extent of injury post-CCI. Representative brain sections (stained with cresyl violet) at 30 days after traumatic brain injury (A). The severe level of CCI (velocity, 5 m/s; depth, 2.0 mm) resulted in substantial injury to the ipsilateral cortex and underlying hippocampus. Mild CCI (velocity, 5 m/s; depth, 1.0 mm) resulted in little macroscopic damage. Lesion volume analysis (B) showed that mice that sustained severe CCI had significantly greater tissue loss than mice that sustained mild CCI or sham procedures. Horizontal bars in (A) represent 1 mm. Pound sign (#) in (B) represents a main effect of injury on lesion volume, Severe CCI>Sham. CCI, controlled cortical impact.